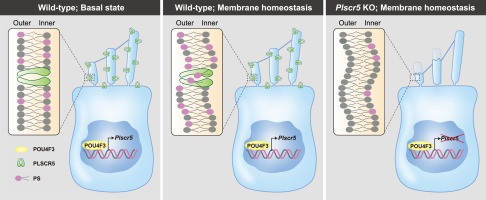
研究人员发现Plscr5是毛细胞功能必需的转录因子POU4F3的下游靶点,其突变与人类DFNA15耳聋有关。Plscr5基因敲除小鼠表现出由于纤毛变性和毛细胞丢失而导致的进行性听力丧失。功能分析表明,Plscr5参与内毛细胞膜磷脂酰丝氨酸外化,特别是内毛细胞磷脂酰丝氨酸外化,对外毛细胞和纤毛的维持具有重要意义。他们的发现强调了PLSCR5作为POU4F3的重要下游效应因子和听觉功能所需的PS外化和膜动力学的调节剂。
据了解,听力依赖于耳蜗毛细胞的结构和功能完整性,特别是其顶端充满F-actin的立体纤毛。磷脂重组酶对维持细胞膜不对称很重要,但其在纤毛立体和听觉功能中的作用尚不完全清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: The phospholipid scramblase PLSCR5 is regulated by POU4F3 and required for hair cell stereocilia homeostasis and auditory functions
Author: Xia Gao, Guang-Jie Zhu, Guoqiang Wan
Issue&Volume: 2025/03/09
Abstract: Hearing relies on the structural and functional integrity of cochlear hair cells, particularly their apical F-actin-filled stereocilia. Phospholipid scramblases are important for maintaining membrane asymmetry, but their roles in the stereocilia and auditory functions are not fully understood. Here, we identify Plscr5 as a downstream target of the transcription factor POU4F3 essential for hair cell function, whose mutation causes human DFNA15 deafness. Plscr5 knockout mice exhibit progressive hearing loss due to stereocilia degeneration and hair cell loss. Functional analyses reveal that PLSCR5 contributes to phosphatidylserine externalization in inner hair cell membranes, particularly in inner hair cells, and is important for outer hair cell and stereocilia maintenance. Our findings highlight PLSCR5 as an important downstream effector of POU4F3 and regulator of PS externalization and membrane dynamics required for auditory functions.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jgg.2025.03.003
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1673852725000724
Journal of Genetics and Genomics:《遗传学报》,创刊于1974年。隶属于爱思唯尔出版集团,最新IF:5.9
官方网址:https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/journal-of-genetics-and-genomics
投稿链接:https://www2.cloud.editorialmanager.com/jgg/default2.aspx
