2025年2月24日出版的《自然—神经科学》杂志发表了中国科学家的一项最新研究成果。来自天津医科大学的于春水团队揭示了早期和晚期社会经济因素对大脑和行为特征的显著影响。
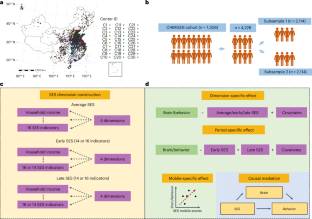
该团队在4228名年轻人中调查了这些影响。从早期(0-10岁)和晚期(10岁)的16个社会经济指标中,该课题组人员构建了家庭、省级、家庭不利和社区不利的社会经济维度。一般而言,家庭SES与大脑结构、连通性及认知功能相关,而家庭不良和邻里不良SES与人格和情绪相关。在早期和晚期SES中观察到大多数关联;然而,调整了早期SES的影响,揭示了晚期特异性SES效应。SES的变化与人格和认知功能有关。小脑和内侧额叶体积以及左额顶叶网络的功能连通性介导了家庭SES与记忆和开放性之间的关联。这些结果既为减少不利的社会经济地位的后果提供了更精确的干预措施,也为排除对人类健康的混杂社会经济影响提供了实验设计。
据介绍,社会经济地位(SES)是一个时变的多维结构,对大脑和行为具有不明确的维度特异性和年龄特异性影响。
附:英文原文
Title: Distinct effects of early-stage and late-stage socioeconomic factors on brain and behavioral traits
Author: Xu, Qiang, Lui, Su, Ji, Yuan, Cheng, Jingliang, Zhang, Long Jiang, Zhang, Bing, Zhu, Wenzhen, Geng, Zuojun, Cui, Guangbin, Zhang, Quan, Liao, Weihua, Yu, Yongqiang, Zhang, Hui, Gao, Bo, Xu, Xiaojun, Han, Tong, Yao, Zhenwei, Qin, Wen, Liu, Feng, Liang, Meng, Fu, Jilian, Xu, Jiayuan, Zhang, Peng, Li, Wei, Shi, Dapeng, Wang, Caihong, Gao, Jia-Hong, Yan, Zhihan, Chen, Feng, Li, Jiance, Zhang, Jing, Wang, Dawei, Shen, Wen, Miao, Yanwei, Xian, Junfang, Wang, Meiyun, Ye, Zhaoxiang, Zhang, Xiaochu, Zuo, Xi-Nian, Xu, Kai, Qiu, Shijun, Yu, Chunshui
Issue&Volume: 2025-02-24
Abstract: Socioeconomic status (SES) is a time-varying multidimensional construct with ill-defined dimension-specific and age-specific effects on brain and behavior. We investigated these effects in 4,228 young adults. From 16 socioeconomic indicators, assessed for early (0–10years) and late (>10years) stages, we constructed family, provincial, family adverse and neighborhood adverse socioeconomic dimensions. Generally, family SES was associated with brain structure and connectivity along with cognitive function, whereas family adverse and neighborhood adverse SES were associated with personality and emotion. Most associations were observed for both early and late-stage SES; however, adjusting for the effect of early stage SES revealed late-stage-specific SES effects. Changes in SES were associated with personality and cognitive function. Cerebellar and medial frontal volumes and functional connectivity within the left frontoparietal network mediated the associations between family SES and memory and openness. These results inform both more precise interventions for reducing the consequences of adverse SES and experimental designs for excluding confounding socioeconomic effects on human health.
DOI: 10.1038/s41593-025-01882-w
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-025-01882-w
Nature Neuroscience:《自然—神经科学》,创刊于1998年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:28.771
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/neuro/
投稿链接:https://mts-nn.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
