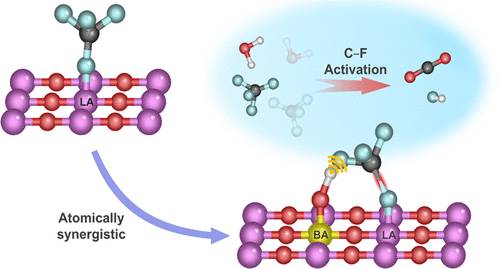
在此,该研究团队通过构建协同的Lewis和Br在原子分散的Zn-O-Al位点上嵌套酸对,以促进C-F键的激活,从而分解典型的PFCs, CF4。密度泛函理论(DFT)计算表明三配位Al (AlIII)和Zn-OH分别具有Lewis和Br在Zn-O-Al上嵌套酸位,协同促进CF4的吸附和分解。x射线吸收光谱(XAS)、吡啶红外光谱(Py-IR)和氨程序升温解吸(NH3-TPD)证实了在原子分散的Zn-O-Al位点上存在AlIII和Zn-OH。CF4-TPD和原位红外光谱证实,Zn-O-Al位点有利于CF4吸附和C-F键活化。结果表明,Zn-O-Al位点具有Lewis和Br嵌套酸对在560°C的低温下实现了100%的CF4分解,并在超过250h的时间内表现出出色的稳定性。
研究人员表示,催化水解是降解全氟化合物(PFCs)的一种可持续的方法,但由于裂解强C-F键所需的高反应温度而受到挑战。
附:英文原文
Title: Promoting C–F Bond Activation for Perfluorinated Compounds Decomposition via Atomically Synergistic Lewis and Brnsted Acid Sites
Author: Wenjie Luo, Kang Liu, Tao Luo, Junwei Fu, Hang Zhang, Chao Ma, Ting-Shan Chan, Cheng-Wei Kao, Zhang Lin, Liyuan Chai, Michelle L. Coote, Min Liu
Issue&Volume: February 19, 2025
Abstract: Catalytic hydrolysis is a sustainable method for the degradation of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) but is challenged by the high reaction temperatures required to cleave strong C–F bonds. Herein, we developed an innovative C–F activation strategy by constructing synergistic Lewis and Brnsted acid pairs over atomically dispersed Zn–O–Al sites to promote C–F bond activation for decomposition of typical PFCs, CF4. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations demonstrate tricoordinated Al (AlIII) sites and Zn–OH functional, respectively, as Lewis and Brnsted acid sites over Zn–O–Al, synergistically enhancing the adsorption and decomposition of CF4. X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), pyridine infrared spectroscopy (Py-IR), and ammonia temperature-programmed desorption (NH3-TPD) verified the presence of both AlIII and Zn–OH on the atomically dispersed Zn–O–Al sites. CF4-TPD and in situ infrared spectroscopy confirmed that the Zn–O–Al sites facilitate CF4 adsorption and C–F bond activation. As a result, the Zn–O–Al sites with synergistic Lewis and Brnsted acid pairs achieved 100% CF4 decomposition at a low temperature of 560 °C and demonstrated outstanding stability for more than 250 h.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c15280
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.4c15280
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
