近日,中国科学院宁波材料技术与工程研究所林杰团队研究了亚纳米级富含氧缺陷的MoO3-x:一种用于无标记超灵敏SERS生物检测的多功能平台。该项研究成果发表在2025年12月24日出版的《结构化学》杂志上。
尽管表面增强拉曼散射(SERS)技术已广泛应用于环境污染物监测与早期癌症诊断等领域,但设计能适应多场景高灵敏度检测的通用型基底仍是亟待解决的难题。
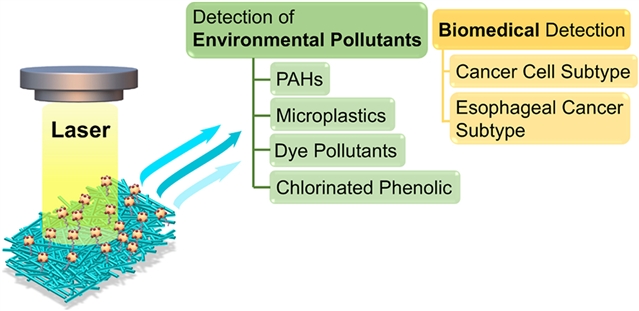
研究组采用创新的缺陷工程策略,成功开发了一种具有高氧空位(Vo)浓度的氧化钼亚纳米线(MoO3-x Sub-NWs)SERS基底。该基底独特地结合了氧空位诱导的梯度缺陷态与一维亚纳米结构产生的量子限域效应,从而实现了化学增强与电磁增强的协同作用。实验结果表明,该基底对罗丹明6G的增强因子高达7.8×107,对甲基橙等染料的检测限达10-11 M,并能有效检测多氯酚、多环芳烃、聚苯乙烯微球等多种环境污染物。
在生物医学应用方面,基于PCA-LDA模型,该方法对肝细胞癌细胞(HepG2)、食管癌细胞(TE-1)与白细胞(WBC)的三分类准确率达92.22%,对食管癌亚型(TE-1与KYSE)的判别准确率达90%,ROC曲线AUC值为0.97。该研究为开发高性能通用型SERS基底提供了新范式,在环境监测与无创肿瘤诊断领域具有重要应用价值。
附:英文原文
Title: Sub-nanoscale oxygen-defect-rich MoO3-x: A versatile platform for label-free ultrasensitive SERS biodetection
Author: anonymous
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-24
Abstract: Although surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) technology has been widely applied in fields such as environmental pollutant monitoring and early cancer diagnosis, the design of universal substrates to enable high-sensitivity detection across multiple scenarios remains a pressing problem to be solved. In this study, an innovative defect engineering strategy was employed to successfully develop a SERS substrate based on molybdenum oxide sub-nanowires (MoO3-x Sub-NWs) with a high oxygen vacancy (Vo) concentration. This substrate uniquely combines the gradient defect states induced by Vo and the quantum confinement effect generated by the one-dimensional sub-nanostructure, thereby achieving the synergy of chemical enhancement and electromagnetic enhancement. Experimental results demonstrate that the substrate exhibits an enhancement factor as high as 7.8×107 for rhodamine 6G, achieves a LOD of 10-11 M for dyes such as methyl orange, and enables effective detection of various environmental pollutants including polychlorinated phenols, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and polystyrene microspheres. In terms of biomedical applications, based on the PCA-LDA model, the method achieves a three-category classification accuracy of 92.22% for hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HepG2), esophageal cancer cells (TE-1), and white blood cells (WBC), a discrimination accuracy of 90% for esophageal cancer subtypes (TE-1 and KYSE), and an ROC curve AUC value of 0.97. This study provides a new paradigm for the development of high-performance universal SERS substrates and possesses significant application value in the fields of environmental monitoring and non-invasive tumor diagnosis.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100848
Source: https://cjsc.ac.cn/cms/issues/950
Chinese Journal of Structural Chemistry:《结构化学》,创刊于1982年。隶属于中国结构化学杂志,最新IF:2.2
官方网址:http://cjsc.ac.cn/
投稿链接:https://www2.cloud.editorialmanager.com/cjschem/default2.aspx
