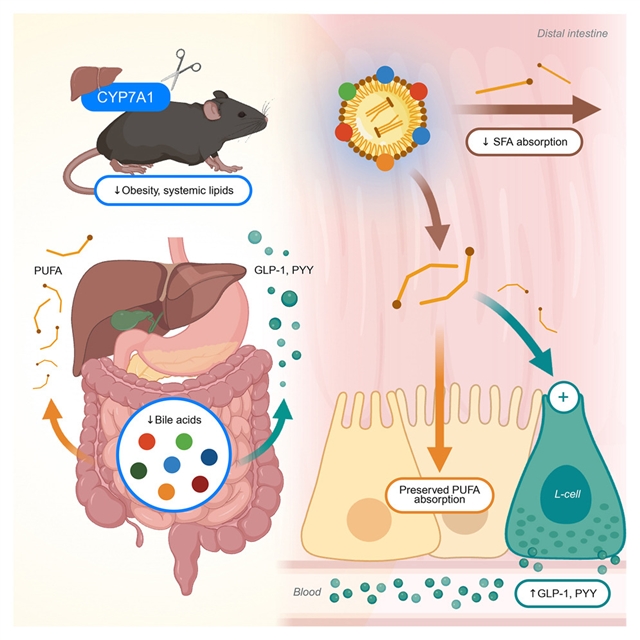
加州大学Thomas Q. de Aguiar Vallim团队取得一项新突破。他们的研究发现胆汁酸通过对脂肪酸吸收的选择性作用调节脂质代谢。2025年12月11日,国际知名学术期刊《细胞—代谢》发表了这一成果。
该课题组研究人员发现胆汁酸在驱动膳食脂肪酸的不同摄取方面的独特而合作的作用。该课题组研究人员首先通过破坏胆汁酸合成中的限速酶Cyp7a1来减少胆汁酸池的大小,从而在小鼠中进行肝脏定向基因编辑。与脂肪酶抑制相比,胆汁酸减少可以预防饮食引起的肥胖,增加厌食激素,抑制过度饮食,改善全身脂质代谢。
值得注意的是,减少胆汁酸选择性地减少了饱和脂肪酸的吸收,但保留了多不饱和脂肪酸。通过靶向其他胆汁酸酶,研究团队确定了单个胆汁酸种类的特定功能。从机理上讲,课题组人员发现胆酸优先将多不饱和脂肪酸溶解成混合胶束以供肠道吸收。他们的研究表明,胆汁酸可以选择性地控制脂肪酸的摄取,为未来对代谢性疾病的干预提供了新的见解。
据了解,肠道脂质吸收是脂肪进入体内的入口,需要胆汁酸和脂肪酶的协同作用。
附:英文原文
Title: Bile acids regulate lipid metabolism through selective actions on fatty acid absorption
Author: Alvin P. Chan, Kelsey E. Jarrett, Rochelle W. Lai, Madelaine C. Brearley-Sholto, Angela S. Cheng, Maria O. Taveras, Anne M. Iwata, Michelle E. Steel, Andrew Lau, Emily C. Whang, John P. Kennelly, Yajing Gao, Gabriella E. Rubert, Heidi M. Schmidt, Emily P. Smith, Baolong Su, Kevin J. Williams, Elizabeth J. Tarling, Thomas Q. de Aguiar Vallim
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-11
Abstract: Intestinal lipid absorption, the entry point for fats into the body, requires the coordinated actions of bile acids and lipases. Here, we uncover distinct yet cooperative roles of bile acids in driving the differential uptake of dietary fatty acids. We first decreased the bile acid pool size by disrupting the rate-limiting enzyme in bile acid synthesis, Cyp7a1, using liver-directed gene editing in mice. Compared with lipase inhibition, reduced bile acids prevented diet-induced obesity, increased anorectic hormones, suppressed excessive eating, and improved systemic lipid metabolism. Remarkably, decreasing bile acids selectively reduced the absorption of saturated fatty acids but preserved polyunsaturated fatty acids. By targeting additional bile acid enzymes, we identified specific functions of individual bile acid species. Mechanistically, we show that cholic acid preferentially solubilizes polyunsaturated fatty acids into mixed micelles for intestinal uptake. Our studies demonstrate that bile acids can selectively control fatty acid uptake, revealing insights for future interventions in metabolic diseases.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2025.11.010
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(25)00494-2
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
