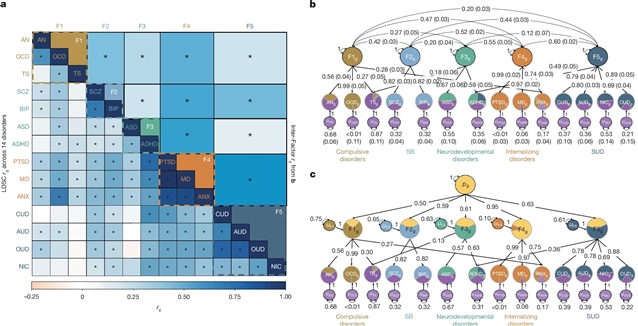
近日,麻省理工学院和哈佛大学博德研究所Jordan W. Smoller及其课题组绘制14种精神疾病的基因图谱。2025年12月10日出版的《自然》发表了这项成果。
在这里,小组通过对14例儿童和成人发病精神疾病(1,056,201例)的一套尖端统计和功能基因组分析进行三角测量来解决这一差距。利用来自常见变异的遗传关联数据,课题组研究人员确定并描述了五个潜在的基因组因素,这些因素解释了个体疾病的大部分遗传变异(平均约66%),并与238个多效位点相关。(1)精神分裂症和双相情感障碍(SB因子);(2)重度抑郁、创伤后应激障碍和焦虑(内化因素)表现出高水平的多基因重叠6和局部遗传相关,很少有疾病特异性位点。所有14种疾病共有的遗传信号在广泛的生物学过程(例如转录调节)中得到了丰富,而在个体因素水平上共享了更具体的途径。跨SB因子的共享遗传信号在兴奋性神经元中表达的基因中大量富集,而内化因子则与少突胶质细胞生物学相关。这些观察结果可能会为神经生物学上更有效的精神病学分类学提供信息,并为设计治疗常见合并症的治疗发展提供目标。
据介绍,精神疾病显示出高水平的合并症和遗传重叠,挑战了当前的诊断界限。对于诸如精神分裂症和双相情感障碍等在诊断分离问题上争议最大的疾病,基因组学方法揭示了大部分遗传信号是共享的。虽然最近的交叉疾病分析已经确定了100多个多效性基因座,但共有的和特定疾病的遗传影响的全部范围仍然不清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: Mapping the genetic landscape across 14 psychiatric disorders
Author: Grotzinger, Andrew D., Werme, Josefin, Peyrot, Wouter J., Frei, Oleksandr, de Leeuw, Christiaan, Bicks, Lucy K., Guo, Qiuyu, Margolis, Michael P., Coombes, Brandon J., Batzler, Anthony, Pazdernik, Vanessa, Biernacka, Joanna M., Andreassen, Ole A., Anttila, Verneri, Brglum, Anders D., Breen, Gerome, Cai, Na, Demontis, Ditte, Edenberg, Howard J., Faraone, Stephen V., Franke, Barbara, Gandal, Michael J., Gelernter, Joel, Hatoum, Alexander S., Hettema, John M., Johnson, Emma C., Jonas, Katherine G., Knowles, James A., Koenen, Karestan C., Maihofer, Adam X., Mallard, Travis T., Mattheisen, Manuel, Mitchell, Karen S., Neale, Benjamin M., Nievergelt, Caroline M., Nurnberger, John I., OConnell, Kevin S., Peterson, Roseann E., Robinson, Elise B., Sanchez-Roige, Sandra S., Santangelo, Susan L., Scharf, Jeremiah M., Stefansson, Hreinn, Stefansson, Kari, Stein, Murray B., Strom, Nora I., Thornton, Laura M., Tucker-Drob, Elliot M., Verhulst, Brad, Waldman, Irwin D.
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-10
Abstract: Psychiatric disorders display high levels of comorbidity and genetic overlap1,2, challenging current diagnostic boundaries. For disorders for which diagnostic separation has been most debated, such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder3, genomic methods have revealed that the majority of genetic signal is shared4. While over a hundred pleiotropic loci have been identified by recent cross-disorder analyses5, the full scope of shared and disorder-specific genetic influences remains poorly defined. Here we addressed this gap by triangulating across a suite of cutting-edge statistical and functional genomic analyses applied to 14 childhood- and adult-onset psychiatric disorders (1,056,201 cases). Using genetic association data from common variants, we identified and characterized five underlying genomic factors that explained the majority of the genetic variance of the individual disorders (around 66% on average) and were associated with 238 pleiotropic loci. The two factors defined by (1) Schizophrenia and bipolar disorders (SB factor); and (2) major depression, PTSD and anxiety (Internalizing factor) showed high levels of polygenic overlap6 and local genetic correlation and very few disorder-specific loci. The genetic signal shared across all 14 disorders was enriched for broad biological processes (for example, transcriptional regulation), while more specific pathways were shared at the level of the individual factors. The shared genetic signal across the SB factor was substantially enriched in genes expressed in excitatory neurons, whereas the Internalizing factor was associated with oligodendrocyte biology. These observations may inform a more neurobiologically valid psychiatric nosology and implicate targets for therapeutic development designed to treat commonly occurring comorbid presentations.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09820-3
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09820-3
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
