近日,浙江师范大学杨发团队研究了在电负性诱导的双金属中心上钯催化CO2加氢生成甲酸的碳酸氢盐依赖性。相关论文于2025年11月4日发表在《美国化学会志》上。
钯表现出接近零的过电位,通过电加氢途径将CO2还原成甲酸,但由于表面CO积累,它会迅速劣化。
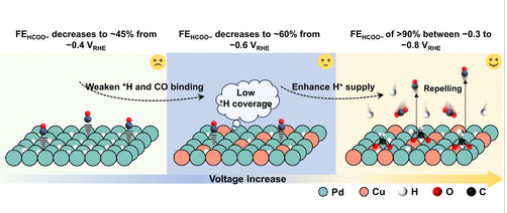
研究组系统地研究了碳酸氢盐电解质在电负性诱导的PdCu双金属中心上调节CO中毒动力学的质子供体能力,测定并定量了钯(合金)在不同电解质中的表面氢吸附和晶格氢吸附特性。结合电子结构分析的理论计算揭示了电负性驱动的电荷重分配,在Pd(Cu)H上诱导带负电荷的Pd和*H吸附原子,d带中心下移,极大地减弱了*CO和*H在Pd位点上的吸附/吸收。动电位x射线衍射、x射线吸收光谱和阳极伏安扫描证实,Cu的加入显著延缓了从α-PdH到β-PdH的电化学相变。
此外,PdCu体系上减弱的* H-Pd相互作用使得富含碳酸氢盐的电解质增强了表面氢的吸附而不是表面下氢的吸附。结合原位红外光谱和微分质谱分析,实验发现浓碳酸氢盐电解质有利于维持较高的*OCHO覆盖率,从而在更宽的电位区间(与可逆氢电极相比为- 0.3 ~ - 0.8 V)内延缓CO的形成。基于自由能谱,研究组发现化学氢化(CH)和质子耦合电子转移(PCET)的首选途径与表面氢覆盖密切相关。此外,在单金属Pd和PdCu体系中,CH路径和PCET路径之间的竞争对表面氢覆盖程度有不同的响应。他们的发现证实了碳酸氢盐电解质是促进Pd(合金)催化的CO2加氢生成甲酸的独特调节因子。
附:英文原文
Title: Bicarbonate-Dependence for Pd-Catalyzed CO2 Hydrogenation to Formate over an Electronegativity-Induced Bimetallic Center
Author: Xuyu Lv, Ting Luo, Chao Lv, Chang Wang, Qianmin Wu, Yanhong Li, Mengjie Wu, Jiuju Feng, Lichun Kong, Jing Zhou, Ai-Jun Wang, Zhengquan Li, De-Li Chen, Fa Yang
Issue&Volume: November 4, 2025
Abstract: Palladium exhibits a near-zero overpotential for CO2 reduction to formate via an electrohydrogenation pathway, but it undergoes a rapid deterioration due to surface CO accumulation. Herein, we conduct a systematic investigation into the bicarbonate electrolyte’s proton-donating capacity in adjusting CO poisoning kinetics over an electronegativity-induced PdCu bimetallic center. The surface-H adsorption and lattice-H absorption features of Pd(alloy) in varying electrolytes are determined and quantified. Theoretical calculations incorporating electronic structure analyses reveal an electronegativity-driven charge redistribution, inducing negatively charged Pd and *H adatoms over the Pd(Cu)H with a downshifted d-band center, which greatly weakens *CO and *H adsorption/absorption onto Pd sites. Potentiodynamic X-ray diffraction, X-ray absorption spectroscopy, and anodic voltammetric scans confirm that the undesired electrochemical phase transition from α-PdH to β-PdH is significantly retarded by the incorporation of Cu. Moreover, the weakened *H–Pd interaction on the PdCu system enables the bicarbonate-rich electrolyte to enhance surface-H adsorption rather than subsurface-H absorption. Combining in situ infrared spectroscopy with differential mass spectrometry, it is experimentally identified that the concentrated bicarbonate electrolyte favors the maintenance of high *OCHO coverage, thereby delaying the formation of CO in a wider potential interval (0.3 to 0.8 V versus a reversible hydrogen electrode). Based on the free energy profiles, we reveal that the preferred route of chemical hydrogenation (CH) and proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) is closely correlated with the surface-H coverage. Moreover, the competition between the CH route and the PCET route on monometallic Pd and PdCu systems exhibits different responses to the degree of surface-H coverage. Our findings establish the bicarbonate electrolyte to be a unique regulatory factor for promoting Pd(alloy)-catalyzed CO2 hydrogenation to formate.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c04023
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c04023
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
