近日,德国马克斯·伯恩非线性光学和短脉冲光谱研究所Evaldas Svirplys团队研究了用于聚焦阿秒脉冲的等离子透镜。相关论文发表在2025年11月4日出版的《自然—光子学》杂志上。
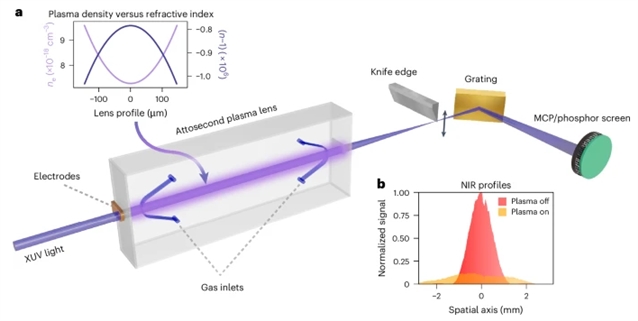
持续时间为阿秒到飞秒的宽带光脉冲为研究时间分辨电子动力学提供了独特的机会。然而,聚焦这些脉冲(通常范围从真空紫外线到软x射线区域)仍然具有挑战性。传统的折射透镜由于色散大、吸收强而不适合使用,而反射光学透镜不受这些问题的困扰,但损耗高。
研究组展示了一种可调谐氢等离子体透镜,能够对能量约20电子伏特及80电子伏特的宽带极紫外阿秒脉冲进行聚焦。模拟结果表明,阿秒脉冲的展宽效应可忽略不计,且在考虑阿秒啁啾的情况下可实现时间压缩。该等离子体透镜的核心优势在于其与高次谐波产生等非线性频率转换过程具有兼容性。基频与谐波频率在聚焦特性上的差异使得这些成分可实现高效分离。因此,高次谐波产生光束线的传输效率可提升至80%以上,这一特性使得该技术特别适用于需要高光子通量的应用场景。
附:英文原文
Title: Plasma lens for focusing attosecond pulses
Author: Svirplys, Evaldas, Jones, Harry, Loisch, Gregor, Thomas, John, Huck, Maryam, Kornilov, Oleg, Garland, Matthew James, Wood, Jonathan C., Vrakking, Marc J. J., Osterhoff, Jens, Schtte, Bernd
Issue&Volume: 2025-11-04
Abstract: Broadband optical pulses with attosecond to femtosecond durations provide unique opportunities for studies of time-resolved electron dynamics. However, focusing these pulses—typically ranging from the vacuum ultraviolet to the soft-X-ray region—remains challenging. Conventional refractive lenses are not suitable owing to large dispersion and strong absorption, whereas reflective optics do not suffer from these issues but have high losses. Here we demonstrate a tunable hydrogen plasma lens to focus broadband extreme-ultraviolet attosecond pulses with energies of around 20eV and 80eV. Simulation results suggest that the stretching of attosecond pulses is negligible, and temporal compression is possible when atto-chirp is included. A key advantage of the plasma lens is its compatibility with nonlinear frequency conversion processes like high-harmonic generation. The different focusing properties of the fundamental and harmonic frequencies allow for an efficient separation of these components. Consequently, the transmission of high-harmonic generation beamlines can be increased to more than 80% and this approach can be suitable for applications requiring high photon flux.
DOI: 10.1038/s41566-025-01794-y
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-025-01794-y
