近日,美国哥伦比亚大学Gaeta, Alexander L.团队研究了基于集成测温的频率稳定纳米光子微腔。这一研究成果于2025年11月3日发表在《自然—光子学》杂志上。
可与电子元件协同封装的现场可部署集成光子器件,将推动光学互联、量子信息处理、精密测量、光谱学和微波生成等重要应用的发展。过去二十年来,光子芯片功能复杂度的提升已取得显著进展,但如何可扩展地克服环境及协同封装电子元件热扰动的影响,仍是亟待解决的关键挑战。
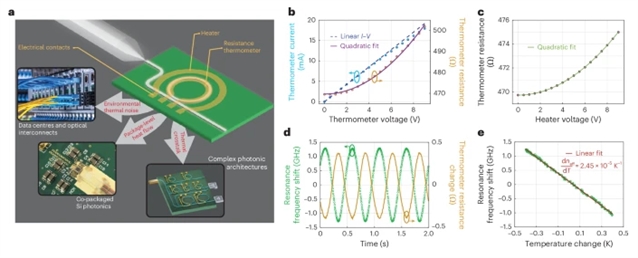
研究组展示了一种全集成方案,可实现硅基高Q值微环谐振腔(作为光子频率基准)的温度监测与稳定控制。该方案通过在微腔上方直接集成薄膜金属电阻作为温度传感器,建立了光学腔绝对共振波长与电阻值的唯一映射关系。经一次性校准后,仅通过电阻测温即可将微谐振腔精确可重复地调谐至目标波长,在数日周期内均方根波长误差小于0.8皮米。
研究组将分布式反馈激光器频率锁定至微谐振腔,在存在显著环境波动的情况下,其中心波长在50小时内波动范围控制在平均值±0.5皮米以内,频率漂移降低48倍,性能优于多数商用的分布式反馈激光器及基于波长锁定器的激光系统。最后,研究组无需光电探测即实现了孤子锁模克尔光梳的稳定运行,这为开发能长期维持锁模状态的克尔光梳光子器件开辟了道路。
附:英文原文
Title: Frequency-stable nanophotonic microcavities via integrated thermometry
Author: Dacha, Sai Kanth, Zhao, Yun, McNulty, Karl J., Bhatt, Gaurang R., Lipson, Michal, Gaeta, Alexander L.
Issue&Volume: 2025-11-03
Abstract: Field-deployable integrated photonic devices co-packaged with electronics will enable important applications such as optical interconnects, quantum information processing, precision measurements, spectroscopy and microwave generation. Significant progress has been made over the past two decades on increasing the functional complexity of photonic chips. However, a critical challenge that remains is the lack of scalable techniques to overcome thermal perturbations arising from the environment and co-packaged electronics. Here we demonstrate a fully integrated scheme to monitor and stabilize the temperature of a high-Q microresonator on a Si-based chip, which can serve as a photonic frequency reference. Our approach relies on a thin-film metallic resistor placed directly above the microcavity, acting as an integrated resistance thermometer, enabling unique mapping of the cavity’s absolute resonance wavelength to the thermometer’s electrical resistance. Following a one-time calibration, the microresonator can be accurately and repeatably tuned to any desired absolute resonance wavelength using thermometry alone with a root-mean-squared wavelength error of <0.8pm over a time span of days. We frequency-lock a distributed feedback laser to the microresonator and demonstrate a 48× reduction in its frequency drift, resulting in its centre wavelength staying within ±0.5pm of the mean over a duration of 50h in the presence of substantial ambient fluctuations, outperforming many commercial distributed feedback and wavelength-locker-based laser systems. Finally, we stabilize a soliton mode-locked Kerr comb without the need for photodetection, paving the way for Kerr-comb-based photonic devices that can potentially operate in the desired mode-locked state indefinitely.
DOI: 10.1038/s41566-025-01789-9
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-025-01789-9
