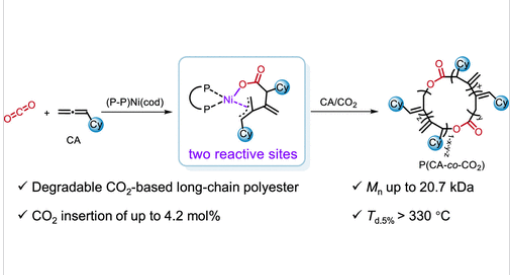
近日,北京大学唐小燕团队报道了镍(0)/膦催化CO2与环己烯共聚制备可降解长链聚酯。相关论文于2025年11月27日发表在《美国化学会志》上。
开发高效策略以实现二氧化碳(CO2)与不饱和烃单体(如烯烃)共聚制备CO2基聚酯具有重要意义,但由于热力学和动力学障碍,该领域仍面临挑战。
研究组首次证实丙二烯类化合物(特别是环己基丙二烯/CA)可作为高效共聚单体,与CO2进行一锅法共聚。采用镍(0)-双齿二芳基膦配合物催化体系,研究组通过氧化加成、配位-插入与还原消除的经典反应序列,实现了CA与CO2的统计共聚,成功制备出具有宽间距酯键结构的长链聚酯P(CA-co-CO2)。通过对膦配体和溶剂的系统调控,发现其在促进CO2插入Ni-C键及后续丙二烯插入Ni-O键的过程中起关键作用,从而驱动高效链增长。值得注意的是,与丙二烯均聚物相比,在聚合物骨架中引入少量CO2可在保持高热稳定性和玻璃化转变温度的同时,显著增强P(CA-co-CO2)的可降解性能。
附:英文原文
Title: Nickel(0)/Phosphine-Catalyzed Copolymerization of CO2 and Cyclohexylallene to Degradable Long-Chain Polyesters
Author: Xi Liao, Xiaoyan Tang
Issue&Volume: November 27, 2025
Abstract: Developing efficient strategies to copolymerize carbon dioxide (CO2) with unsaturated hydrocarbon monomers, such as olefins, to produce CO2-based polyesters is highly desirable but remains challenging owing to thermodynamic and kinetic barriers. Herein, we demonstrate that allenes, specifically cyclohexylallene (CA), serve as effective comonomers for one-pot copolymerization with CO2. Using a nickel(0)–bidentate diarylphosphine complex, we achieve the statistical copolymerization of CA and CO2 to deliver long-chain polyester P(CA-co-CO2) with widely spaced ester linkages, via a classical sequence of oxidative addition, coordination–insertion, and reductive elimination. Systematic tuning of both phosphine ligand and solvent reveals their crucial roles in facilitating CO2 insertion into the Ni–C bond and subsequent allene insertion into the Ni–O bond, thereby driving efficient chain propagation. Notably, incorporation of a small amount of CO2 into the polymer backbone enhances the degradability of P(CA-co-CO2) while preserving its high thermal stability and glass-transition temperature, compared with the allene homopolymer.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c14970
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c14970
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
