近日,上海交通大学么艳彩团队实现了电化学短程反硝化-化学重氮处理低碳硝酸盐废水。相关论文于2025年11月26日发表在《德国应用化学》杂志上。
如何实现低碳高效处理硝酸盐(NO3-)废水是一大难题,因为传统的多效蒸发和生物反硝化均为高碳排工艺,尤其当NO3-浓度超过1000 mg-N·L-1时更是如此。
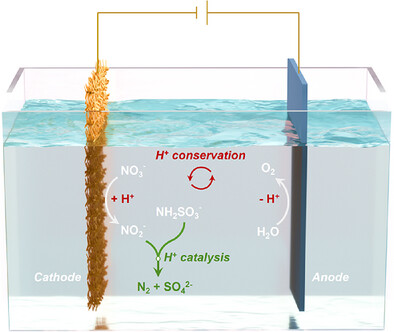
研究组提出一种低碳高效脱氮策略,通过将电化学短程反硝化(NO3-→NO2-转化)与化学重氮化耦合(ESD-CD),先采用氧化物衍生泡沫铜电极将NO3-电化学还原为NO2-,再通过氨基磺酸(NH2SO3-)化学重氮化反应快速生成氮气。针对5000 mg-N·L-1模拟硝酸盐废水,ESD-CD技术可实现98.8%的NO3-去除率、99.9%的氮气选择性与95.3%的法拉第效率。其能耗低至9.97 kWh·kg-N-1,脱氮速率更是达到创纪录的24.87 g-N·m-2·h-1。
在光伏驱动下,该技术处理工业硝酸盐废水(3085.2 mg-N·L-1)时保持稳定性能:NO3-去除率超96.6%,氮气选择性达99.2%;与生物反硝化和多效蒸发相比,运行成本分别降低64.4%和74.9%,二氧化碳排放削减79.5%和93.3%。这项研究充分证明,将选择性电化学硝酸盐还原与化学重氮化耦合,可为高浓度硝酸盐废水的可持续处理提供创新解决方案。
附:英文原文
Title: Electrochemical Shortcut Denitrification Coupled with Chemical Diazotization for Low-Carbon Nitrate Wastewater Treatment
Author: Weixing Zhang, Furong Guo, Weiting Gong, Di Yang, Xia Yin, Falong Jia, Wendong Wei, Yancai Yao, Lizhi Zhang
Issue&Volume: 2025-11-26
Abstract: Efficient treatment of nitrate (NO3) wastewater with low carbon emission is a tough challenge because traditional multiple-effect evaporation and biological denitrification are carbon-intensive, especially in the case of NO3 concentration higher than 1000 mg-N L1. In this study, we demonstrate a low-carbon and high-energy-efficiency denitrification strategy by coupling electrochemical shortcut denitrification (NO3-to-NO2 conversion) with chemical diazotization (ESD-CD), where NO3 is first electrochemically reduced to NO2 by an oxide-derived Cu foam electrode, which then reacts with sulfamate (NH2SO3) via chemical diazotization to rapidly generate N2. For 5000 mg-N L1 simulated NO3 wastewater, the ESD-CD achieved 98.8% NO3 removal efficiency, 99.9% N2 selectivity, and 95.3% Faradaic efficiency. Impressively, its energy consumption was as low as 9.97 kWh kg-N1, and its denitrification rate reached an unprecedented record of 24.87 g-N m2 h1. Driven by photovoltaic cells, the ESD-CD process maintained stable performance in treating industrial NO3 wastewater (3085.2 mg-N L1) with over 96.6% NO3 removal efficiency and 99.2% N2 selectivity, and also reduced operational costs by 64.4% and 74.9%, and CO2 emissions by 79.5% and 93.3% in comparison with biological denitrification and multiple-effect evaporation, underscoring the promising potential of coupling selective electrochemical NO3 reduction with chemical diazotization for sustainable treatment of high-concentration NO3 wastewater.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202516226
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202516226
Angewandte Chemie:《德国应用化学》,创刊于1887年。隶属于德国化学会,最新IF:16.823
官方网址:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/15213773
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/anie/default.aspx
