近日,美国英特尔公司Mateusz T. M?dzik团队实现了并行操作两个纯交换量子比特。相关论文于2025年11月26日发表在《自然》杂志上。
半导体是实现大规模量子计算机最有前景的平台之一,因为先进制造技术可制备大规模量子点阵列。在这些量子点阵列上可采用多种量子比特编码方式来存储和操控量子信息。无论采用何种编码方式,精确控制阵列中量子点所囚禁电子之间的交换相互作用都至关重要。此外,为充分利用单个量子比特有限的相干性,必须能够并行执行高保真度的量子操作。
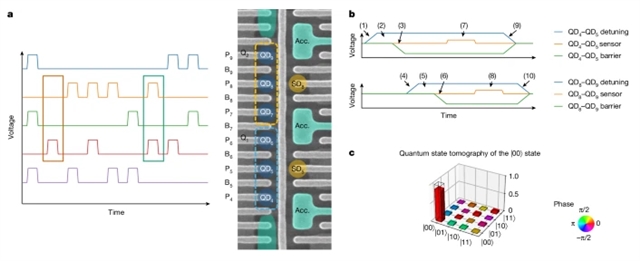
研究组展示了两个纯交换量子比特的并行操作,该量子比特由线性排列的六个量子点构成。通过随机基准测试(RB)技术,研究组证明以最大并行方式对五个势垒门施加脉冲以调制交换相互作用,可保持与顺序操作相当的量子比特控制质量。为实现并行交换脉冲而开发的技术可直接拓展到其他基于量子点的编码方案。此外,研究组首次实验演示了纯交换量子比特的iSWAP门以及电荷锁定的泡利自旋阻塞(PSB)读出方法。结果通过交叉熵基准测试(XEB)验证,该技术对大规模量子计算系统的性能表征非常有用;此处是首次应用于基于半导体技术的量子系统。
附:英文原文
Title: Operating two exchange-only qubits in parallel
Author: Mdzik, Mateusz T., Luthi, Florian, Guerreschi, Gian Giacomo, Mohiyaddin, Fahd A., Borjans, Felix, Chadwick, Jason D., Curry, Matthew J., Ziegler, Joshua, Atanasov, Sarah, Bavdaz, Peter L., Connors, Elliot J., Corrigan, J., Ercan, H. Ekmel, Flory, Robert, George, Hubert C., Harpt, Benjamin, Henry, Eric, Islam, Mohammad M., Khammassi, Nader, Keith, Daniel, Lampert, Lester F., Mladenov, Todor M., Morris, Randy W., Nethwewala, Aditi, Neyens, Samuel, Otten, Ren, Osuna Ibarra, Linda P., Patra, Bishnu, Pillarisetty, Ravi, Premaratne, Shavindra, Ramsey, Mick, Risinger, Andrew, Rooney, John D., Savytskyy, Rostyslav, Watson, Thomas F., Zietz, Otto K., Matsuura, Anne Y., Pellerano, Stefano, Bishop, Nathaniel C., Roberts, Jeanette, Clarke, James S.
Issue&Volume: 2025-11-26
Abstract: Semiconductors are among the most promising platforms to implement large-scale quantum computers, as advanced manufacturing techniques allow fabrication of large quantum dot arrays1. Various qubit encodings can be used to store and manipulate quantum information on these quantum dot arrays. Regardless of qubit encoding, precise control over the exchange interaction between electrons confined in quantum dots in the array is critical. Furthermore, it is necessary to execute high-fidelity quantum operations concurrently to make full use of the limited coherence of individual qubits. Here we demonstrate the parallel operation of two exchange-only qubits, consisting of six quantum dots in a linear arrangement. Using randomized benchmarking (RB) techniques, we show that issuing pulses on the five barrier gates to modulate exchange interactions in a maximally parallel way maintains the quality of qubit control relative to sequential operation. The techniques developed to perform parallel exchange pulses can be readily adapted to other quantum-dot-based encodings. Moreover, we show the first, to our knowledge, experimental demonstrations of an iSWAP gate for exchange-only qubits and of a charge-locking Pauli spin blockade (PSB) readout method. The results are validated using cross-entropy benchmarking (XEB)2, a technique useful for performance characterization of larger quantum computing systems; here it is used for the first time on a quantum system based on semiconductor technology. Parallel operation of two exchange-only qubits consisting of six quantum dots arranged linearly is shown to be achievable and maintains qubit control quality compared with sequential operation, with potential for use in scaled quantum computing.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09767-5
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09767-5
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
