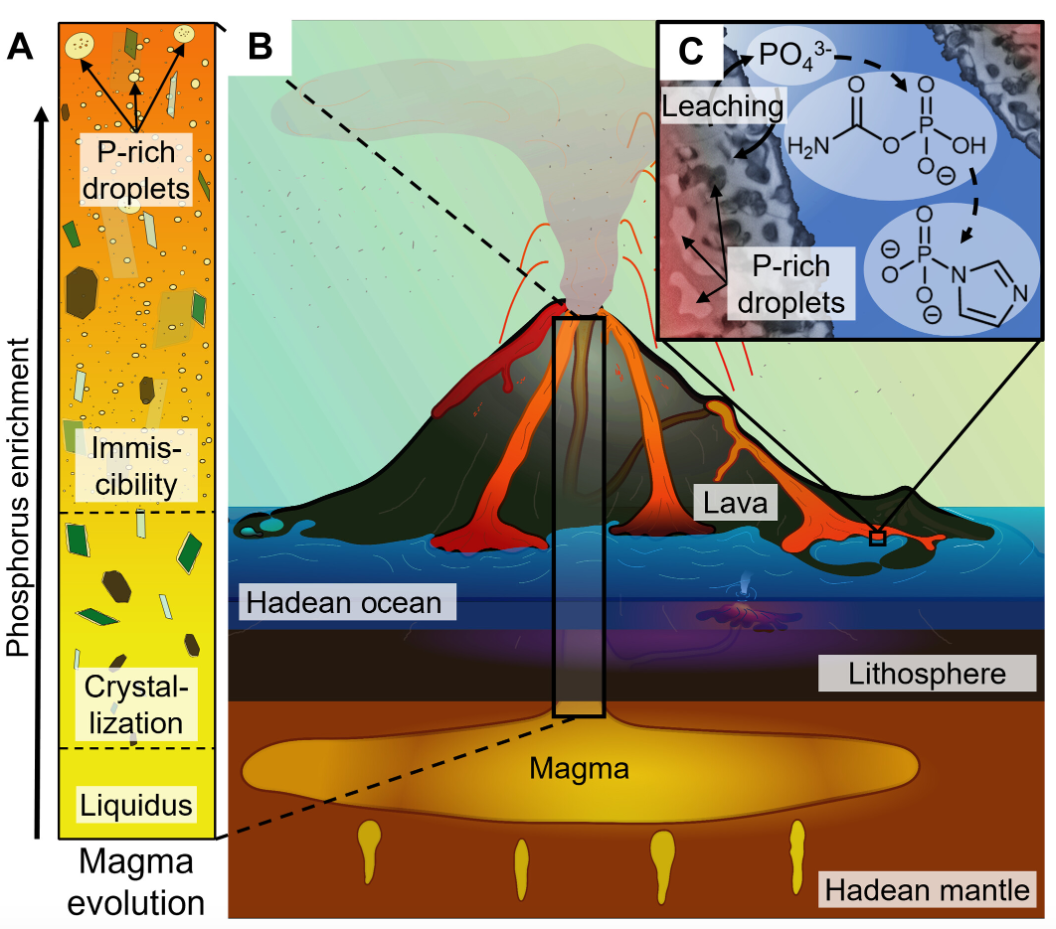
近日,德国路德维希马克西米利安大学Bettina Scheu团队揭示了岩浆的不混溶性为生命前化学提供了磷酸盐。该项研究成果发表在2025年11月21日出版的《科学-进展》杂志上。
磷是现存生命及生命起源的必需元素。然而地表磷酸盐的低丰度及含磷矿物较差的水溶性,构成了生命起源前化学的重要障碍。
研究组揭示火山熔岩中的硅酸盐-磷酸盐不混溶现象,可为磷的局部富集提供一种广泛存在的机制。通过实验发现,从富磷的太古代熔岩出发,快速冷却会形成富含五氧化二磷可达21wt%的不混溶玻璃质微珠,这些微珠可通过火山作用输送到地表。
在水相浸取实验中研究组测得毫摩尔级的磷酸盐浓度,该浓度条件下可合成多聚磷酸盐、磷酸化咪唑等磷酸化试剂,产率最高可达34%。这些结果表明火山作用能够有效富集磷酸盐,从而为生命起源前化学反应提供驱动力。
附:英文原文
Title: Magmatic immiscibility provides phosphate for prebiotic chemistry
Author: Daniel Weller, Thomas Matreux, Iris B. A. Smokers, Almuth Schmid, Christof B. Mast, Donald B. Dingwell, Dieter Braun, Bettina Scheu
Issue&Volume: 2025-11-21
Abstract: Phosphorus is essential for extant and nascent life. However, phosphate’s low terrestrial abundance and the poor aqueous solubility of phosphorus-bearing minerals pose major hurdles for prebiotic chemistry. Here, we show that silicate-phosphate immiscibility in volcanic melts could have provided a widely available mechanism for the local enrichment of phosphate. Starting with a phosphorus-enriched Archean melt, we observe that rapid cooling results in the formation of immiscible glassy droplets with up to 21 weight % phosphorus pentoxide, which can be delivered to the surface by volcanic processes. In aqueous leaching, we detect millimolar phosphate concentrations, which enable the synthesis of phosphorylating agents such as polyphosphates and imidazole phosphate with up to 34% yield. These results demonstrate how volcanic processes can enrich phosphate to fuel prebiotic chemistry.
DOI: adz2567
Source: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adz2567
