宾夕法尼亚大学J. Nicholas Betley小组宣布他们研制了一个控制疼痛需要状态的臂旁中枢。相关论文于2025年10月8日发表在《自然》杂志上。
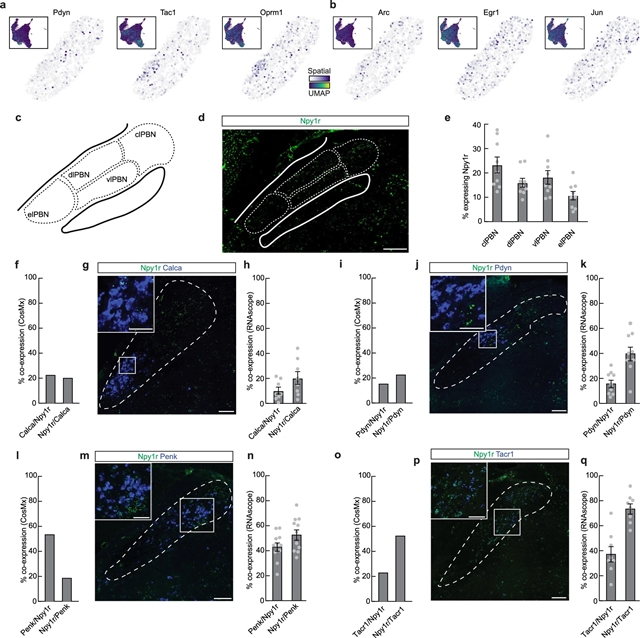
在这里,研究人员以空间转录组学、神经操作、活动记录和计算模型为主题,证明了在解剖学和分子上多样化的臂旁神经元中,表达神经肽Y (NPY)受体Y1 (Y1R神经元)的活性在损伤后增加,并预测了功能性应对行为。无论损伤类型如何,饥饿、口渴或捕食者线索都能通过释放NPY抑制臂旁Y1R神经元,从而抑制持续性疼痛。总之,他们的研究结果表明,在疼痛反应的臂旁Y1R神经元中存在内源性镇痛中枢。
据悉,急性身体损伤后的长期持续疼痛是慢性疼痛的一个显著特征。在脊髓和大脑的几个核中已经发现了对氧刺激或组织损伤迅速反应的神经元群。了解持续疼痛(包括组织愈合后)信号的中心机制仍然是一个挑战。
附:英文原文
Title: A parabrachial hub for need-state control of enduring pain
Author: Goldstein, Nitsan, Maes, Amadeus, Allen, Heather N., Nelson, Tyler S., Kruger, Kayla A., Kindel, Morgan, Yeung, Albert T. M., Smith, Nicholas K., Carty, Jamie R. E., Boccia, Lavinia, Blank, Niklas, Lo, Emily, Villari, Rachael E., Cho, Ella, Marble, Erin L., Awh, Michelle, Dumiaty, Yasmina, Chee, Melissa J., Khanna, Rajesh, Thaiss, Christoph A., Taylor, Bradley K., Kennedy, Ann, Betley, J. Nicholas
Issue&Volume: 2025-10-08
Abstract: Long-term sustained pain following acute physical injury is a prominent feature of chronic pain conditions1. Populations of neurons that rapidly respond to noxious stimuli or tissue damage have been identified in the spinal cord and several nuclei in the brain2,3,4. Understanding the central mechanisms that signal ongoing sustained pain, including after tissue healing, remains a challenge5. Here we use spatial transcriptomics, neural manipulations, activity recordings and computational modelling to demonstrate that activity in an ensemble of anatomically and molecularly diverse parabrachial neurons that express the neuropeptide Y (NPY) receptor Y1 (Y1R neurons) is increased following injury and predicts functional coping behaviour. Hunger, thirst or predator cues suppressed sustained pain, regardless of the injury type, by inhibiting parabrachial Y1R neurons via the release of NPY. Together, our results demonstrate an endogenous analgesic hub at pain-responsive parabrachial Y1R neurons.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09602-x
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09602-x
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
