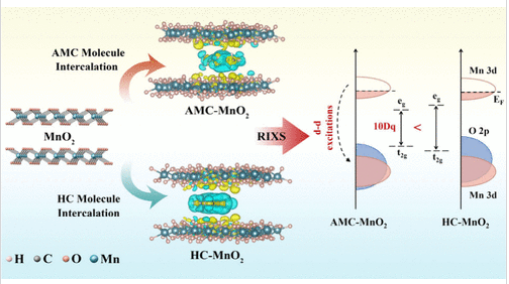
近日,中国科学技术大学宋礼团队报道了通过电子调谐分子插入剂促进二氧化锰阴极中的离子传输。2025年10月30日出版的《美国化学会志》发表了这项成果。
水基锌离子电池正极材料的层间工程研究越来越广泛。然而,目前的工作主要集中在主体材料的结构修饰上,对插层剂的分子性质关注有限。
研究组在二氧化锰中引入了两种具有吸电子基团和供电子基团相对功能化的有机分子插层剂来调节阴极的本征电子结构。共振非弹性x射线散射(RIXS)光谱分析表明,两种插层剂对Mn三维轨道的调节程度不同。与供电子基团相比,吸电子基团加强了与晶格氧的相互作用,促进了Mn的3d-O 2p轨道杂化,导致晶体场分裂能降低,与Zn的相互作用增强。
结果,具有吸电子基团插入MnO2的分子表现出更好的离子传输动力学,与供电子分子相比,离子扩散值增加了10倍,并且具有优异的速率性能(在8℃时为172.7 mA h g-1),比商用MnO2高出10.3倍。值得注意的是,原位和非原位x射线技术证实了循环过程中可逆和稳定的层间结构演变,这归因于带有吸电子基团的分子嵌入Zn和MnO2之间的强相互作用。该研究为层状材料的分子级电子调制提供了新的见解。
附:英文原文
Title: Boosting Ion Transport in Manganese Dioxide Cathodes through Electronically Tuned Molecular Intercalants
Author: Yixiu Wang, Heng Zhou, Shiqiang Wei, Shuangming Chen, Dengfeng Cao, Quan Zhou, Xiaojun Wu, Li Song
Issue&Volume: October 30, 2025
Abstract: Interlayer engineering has been extensively investigated in cathode materials for aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AZIBs). However, current efforts have primarily focused on structural modifications of host materials with limited attention to the molecular properties of intercalants. Herein, we introduce two types of organic molecular intercalants, relatively functionalized with electron-withdrawing groups and electron-donating groups, into MnO2 to modulate the cathode’s intrinsic electronic structure. Resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) spectroscopy reveals that both intercalants regulate Mn 3d orbitals to different extents. In contrast to the electron-donating group, the electron-withdrawing groups strengthen the interactions with lattice oxygen and promote the Mn 3d–O 2p orbital hybridization, resulting in a reduced crystal field splitting energy and enhanced interactions with Zn. As a result, the molecule with electron-withdrawing groups intercalated with MnO2 exhibits improved ion transport kinetics, delivering a 10-fold increase in the ionic diffusion value as compared to the electron-donating one, and excellent rate performance (172.7 mA h g–1 at 8 C) outperforming commercial MnO2 by a factor of 10.3. Notably, in situ and ex situ X-ray techniques confirm the reversible and stable interlayer structure evolution during cycling, attributed to the strong interaction between Zn and MnO2 intercalated by molecules with electron-withdrawing groups. This study provides new insights into molecular-level electronic modulation in layered materials toward advanced cathode materials.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c08301
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c08301
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
