近日,天津大学董少强团队研究了TTM二自由基中自旋控制的双发射:解开单重态和三重态荧光途径的相互作用。2025年10月20日,《美国化学会志》发表了这一成果。
控制发光双自由基的光物理机制,特别是它们的单线态和三重态发射之间的相互作用,目前仍不清楚。
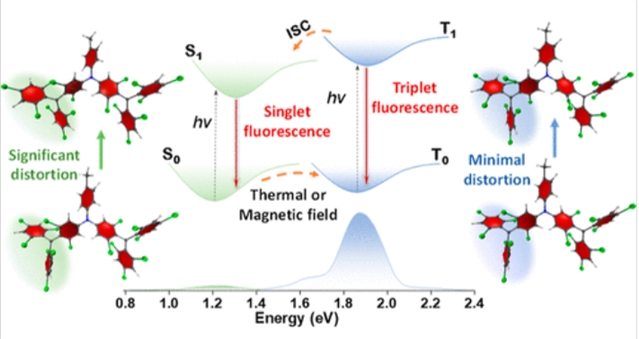
研究组报道了基于三(2,4,6-三氯苯基)甲基(TTM)支架的三个发光自由基,单自由基MTA和双自由基DTA和DTA(t-Bu)2。实验结果和DFT计算表明,两种双根类化合物具有不同的S1→S0(第一激发单重态到单重态基态)和T1→T0(第一激发三重态到三重态基态)荧光辐射途径,而单根MTA仅具有D1→D0(第一激发双重态到双重态基态)荧光辐射途径。变温电子自旋共振测量显示DTA和DTA(t-Bu)2的单重态基态和热可达三重态基态,ΔES-T值分别为0.33和0.35 kcal/mol。基于ΔES-T值的Boltzmann种群分析表明,在298 K时,DTA和DTA(t-Bu)2的单重态和三重态共存,其中S0态占63.6%,DTA(t-Bu)2占64.4%,对应的T0态种群分别为36.4%和35.6%。
此外,两种双根碱在100 K附近表现出最大的磁致发光现象,反映了热能和磁场诱导的S0→T0自旋转换的协同相互作用。值得注意的是,两种双根碱的温度依赖性光致发光实验揭示了两种双根碱的双重发射行为:从298到78 K冷却在~690 nm处逐渐抑制三态荧光,而在900 nm以上的近红外区域增强弱单态荧光。两种双根碱的外部重原子效应也表现出分子内系统间从T1到S1的交叉。
此外,理论激发态构象分析表明,与S1→S0跃迁相比,两种二自由基类化合物在T1→T0跃迁过程中具有明显的结构保存性,重组能更小,高频振动更弱,辐射跃迁速率常数更小。该工作建立了对TTM双根碱系统中自旋控制双荧光的全面理解,为开发具有可调自旋控制发射特性的高自旋发光材料提供了关键的设计原则。
附:英文原文
Title: Deciphering Spin-Governed Dual Emissions in TTM Diradicaloids: Unraveling the Interplay of Singlet and Triplet Fluorescence Pathways
Author: Zekun Tong, Shuo Zhang, Weiwei Niu, Tingxi Yu, Xinfang Zhang, Penglei Yao, Jinfeng Wang, Yibo Han, Guangwu Li, Shaoqiang Dong
Issue&Volume: October 20, 2025
Abstract: The photophysical mechanisms governing luminescent diradicals, particularly the interplay between their singlet and triplet emissions, remain incompletely understood. Herein, we report three luminescent radicals, monoradical MTA and diradical DTA and DTA(t-Bu)2, based on a tris(2,4,6-trichlorophenyl)methyl (TTM) scaffold. Experimental results and DFT calculations demonstrated the dual emission mechanism of two diradicaloids with distinct S1 → S0 (first excited singlet state to singlet ground state) and T1 → T0 (first excited triplet state to triplet ground state) fluorescent radiative pathways, while monoradical MTA shows only doublet emission with a D1 → D0 (first excited doublet state to doublet ground state) fluorescent radiative pathway. Varying-temperature electron spin resonance measurements revealed the singlet ground state and thermal accessible triplet ground state of DTA and DTA(t-Bu)2, with ΔES–T values of 0.33 and 0.35 kcal/mol, respectively. Boltzmann population analysis based on the ΔES–T values reveals the coexistence of singlet and triplet states at 298 K, with the S0 state predominating at 63.6% for DTA and 64.4% for DTA(t-Bu)2, while the corresponding T0 state populations are 36.4% and 35.6%, respectively. Moreover, two diradicaloids exhibit maximum magnetoluminescence phenomena near 100 K, reflecting the synergistic interplay of thermal energy and magnetic-field-induced S0 → T0 spin conversion. Notably, temperature-dependent photoluminescent experiments of two diradicaloids unveiled the dual emission behavior of two diradicaloids: cooling from 298 to 78 K progressively suppressed triplet fluorescence at ~690 nm while it enhanced weak singlet fluorescence in the near-infrared region beyond 900 nm. External heavy-atom effects of two diradicaloids also demonstrated intramolecular intersystem crossing from T1 to S1. Furthermore, theoretical excited-state conformation analysis on two diradicaloids revealed their distinct structural preservation during T1 → T0 transitions compared to S1 → S0 transitions, which is also confirmed by the smaller reorganization energy, weaker high-frequency vibrations, and smaller radiative transition rate constant. Our work establishes a comprehensive understanding of spin-governed dual fluorescence in TTM diradicaloid systems, providing critical design principles for developing high-spin luminescent materials with tunable spin-controlled emission properties.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c10608
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c10608
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
