近日, 美国俄勒冈州立大学Peter U. Clark团队研究了过去450万年的全球平均海平面。2025年10月16日出版的《科学》杂志发表了这项成果。
晚新生代全球平均海平面的变化幅度仍存在争议。
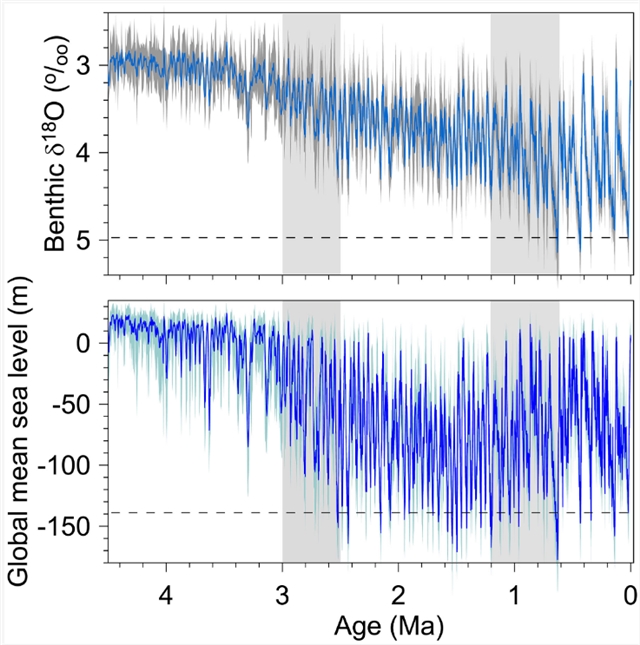
研究组通过重建海水δ18O变化,再现了450万年前至今的全球平均海平面变化曲线,该模型考虑了温度对全球冰盖δ18O值的影响。在450万至300万年前期间,海平面高值期始终比现今高出20米;而首次低于现今的低值期出现于400万年前,这标志着北半球冰川作用开始启动。
全球冰川作用在300万至250万年前期间持续增强,其最低海平面达到与2.1万年前末次盛冰期相当的水平,此类极低海平面在更新世多次重现。研究组将中更新世冰盖变率转型期(120万至62万年前)归因于:随着约10万年周期CO2变率增强,其对4.1万年周期斜率强迫产生的调制效应。
附:英文原文
Title: Global mean sea level over the past 4.5 million years
Author: Peter U. Clark, Jeremy D. Shakun, Yair Rosenthal, David Pollard, Steven W. Hostetler, Peter Khler, Patrick J. Bartlein, Jonathan M. Gregory, Chenyu Zhu, Daniel P. Schrag, Zhengyu Liu, Nicklas G. Pisias
Issue&Volume: 2025-10-16
Abstract: Changes in global mean sea level (GMSL) during the late Cenozoic remain uncertain. We use a reconstruction of changes in δ18O of seawater to reconstruct GMSL since 4.5 million years ago (Ma) that accounts for temperature-driven changes in the δ18O of global ice sheets. Between 4.5 and 3 Ma, sea level highstands remained up to 20 m above present whereas the first lowstands below present suggest onset of Northern Hemisphere glaciation at 4 Ma. Intensification of global glaciation occurred from 3 Ma to 2.5 Ma, culminating in lowstands similar to the Last Glacial Maximum lowstand at 21,000 years ago and that reoccurred throughout much of the Pleistocene. We attribute the middle Pleistocene transition in ice sheet variability (1.2 Ma to 0.62 Ma) to modulation of 41-thousand-year (kyr) obliquity forcing by an increase in ~100-kyr CO2 variability.
DOI: adv8389
Source: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adv8389
