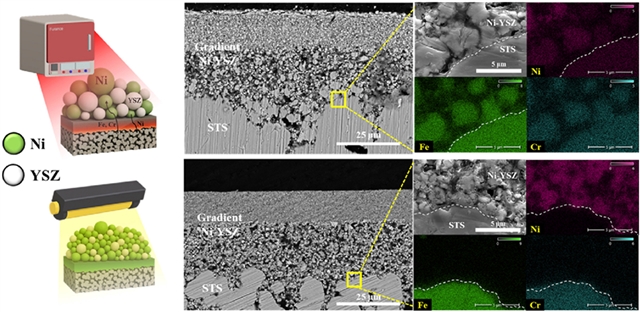
近日,韩国汉阳大学Young-Beom Kim团队报道了闪光烧结提高金属负载固体氧化物燃料电池(MS-SOFCs)镍基电极的电化学性能。这一研究成果于2025年10月9日发表在《结构化学》杂志上。
金属支撑固体氧化物燃料电池(MS-SOFCs)作为一种先进的固体氧化物燃料电池技术,由于其优异的机械稳定性、易于操作和高可制造性,近年来受到了广泛的关注。金属衬底的应用可以提高热循环和氧化还原循环下的耐久性,并实现更薄的电解质层,有助于增强性能。然而,其制造通常需要高温烧结以确保足够的材料性能和附着力,因为大多数SOFC组件是陶瓷的。这些高温过程可能导致不良影响,包括金属载体氧化、化学副反应和加速颗粒生长,从而降低电池性能。
研究组介绍了一种超快速烧结方法,通过将不锈钢金属支架与镍钇稳定氧化锆(Ni-YSZ)复合阳极活性层直接集成,制造MS-SOFC。闪光烧结是一种创新的超快速技术,它有效地抑制了Ni催化剂颗粒的生长,扩大了电化学反应面积,同时最大限度地减少了金属支撑层和阳极层之间的材料扩散。结果表明,制备的电池在650°C下具有超过1 V的稳定开路电压(OCV)和412 mW/cm2的峰值功率密度,比传统烧结电池的性能提高了约426.3%。这项研究提出了SOFC制造的变革战略,解决了传统长时间热处理的挑战,并展示了推进能量转换技术的巨大潜力。
附:英文原文
Title: Enhancing the electrochemical performance of Ni-based electrodes via flash light sintering for metal-supported solid oxide fuel cells (MS-SOFCs)
Author: anonymous
Issue&Volume: 2025-10-09
Abstract: Metal-supported solid oxide fuel cells (MS-SOFCs) have recently gained significant attention as an advanced SOFC technology, owing to their excellent mechanical robustness, ease of handling, and high manufacturability. The use of metal substrates enables improved durability under thermal and redox cycling, and allows for thinner electrolyte layers, contributing to enhanced performance. However, their fabrication typically requires high-temperature sintering to ensure adequate material properties and adhesion, as most SOFC components are ceramic. These high-temperature processes can lead to undesirable effects, including metal support oxidation, chemical side reactions, and accelerated particle growth, which degrade cell performance. This study introduces an ultra-fast sintering approach for MS-SOFC fabrication by directly integrating stainless-steel metal supports with nickel–yttria-stabilized zirconia (Ni-YSZ) composite anode active layers. The application of flash light sintering—an innovative ultra-fast technique—effectively suppressed Ni catalyst particle growth, expanding the electrochemical reaction area while minimizing material diffusion between the metal support and anode layer. As a result, the fabricated cells achieved a stable open-circuit voltage (OCV) exceeding 1 V at 650 °C and a peak power density of 412 mW/cm2, representing an approximately 426.3% performance improvement over conventionally sintered cells. This research presents a transformative strategy for SOFC manufacturing, addressing the challenges of conventional long-duration heat treatments and demonstrating significant potential for advancing energy conversion technologies.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100758
Source: https://cjsc.ac.cn/cms/issues/895
Chinese Journal of Structural Chemistry:《结构化学》,创刊于1982年。隶属于中国结构化学杂志,最新IF:2.2
官方网址:http://cjsc.ac.cn/
投稿链接:https://www2.cloud.editorialmanager.com/cjschem/default2.aspx
