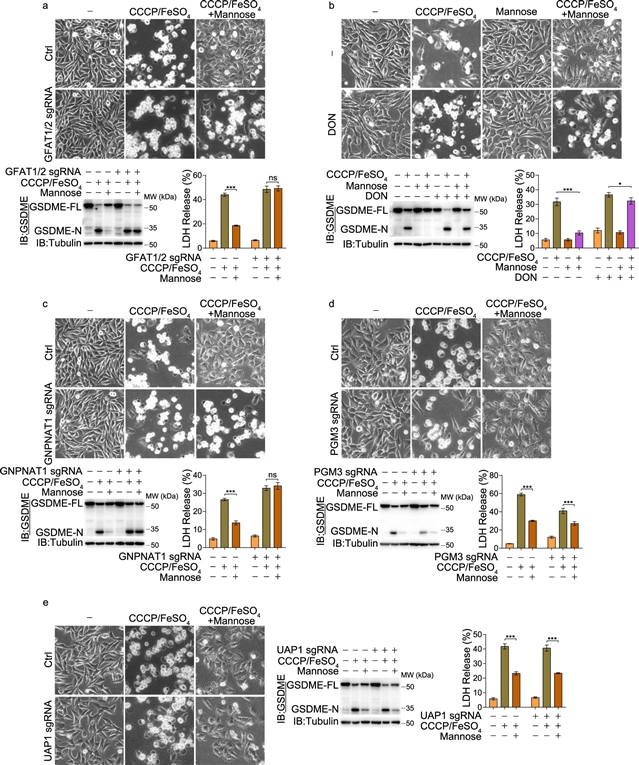
厦门大学吴乔课题组发现,甘露糖通过代谢产物N -乙酰氨基葡萄糖-6-磷酸(GlcNAc-6P)激活的AMPK拮抗GSDME介导的焦亡。相关论文于2023年7月17日发表在《细胞研究》杂志上。
他们证明甘露糖,一种己糖,通过激活AMP激活的蛋白激酶(AMPK)抑制GSDME介导的焦亡。从机制上说,己糖胺生物合成途径中的甘露糖代谢增加了代谢物GlcNAc-6P的水平,该代谢物与AMPK结合,促进了LKB1对AMPK的磷酸化。激活的AMPK随后磷酸化GSDME的Thr6位点,从而阻断caspase-3诱导的GSDME切割,从而抑制焦亡。AMPK介导的GSDME磷酸化的调节作用在AMPK敲除和GSDMET6E或GSDMET6A敲入小鼠中得到进一步证实。
在小鼠原发性肿瘤模型中,甘露糖抑制小肠和肾脏的焦亡,减轻顺铂或奥沙利铂诱导的组织毒性,而不减弱抗肿瘤作用。甘露糖的保护作用也在一小群接受正常化疗的胃肠道癌症患者中得到证实。他们的研究揭示了甘露糖通过GlcNAc-6P介导的AMPK活化拮抗GSDME介导的焦亡的新机制,并提示甘露糖补充在临床应用中减轻化疗引起的副作用的效用。
据了解,焦亡是一种由气皮蛋白家族成员执行的受调节的细胞死亡。然而,如何负调控气凝胶介导的焦亡仍不清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: Mannose antagonizes GSDME-mediated pyroptosis through AMPK activated by metabolite GlcNAc-6P
Author: Ai, Yuan-li, Wang, Wei-jia, Liu, Fan-jian, Fang, Wei, Chen, Hang-zi, Wu, Liu-zheng, Hong, Xuehui, Zhu, Yuekun, Zhang, Ci-xiong, Liu, Long-yu, Hong, Wen-bin, Zhou, Bo, Chen, Qi-tao, Wu, Qiao
Issue&Volume: 2023-07-17
Abstract: Pyroptosis is a type of regulated cell death executed by gasdermin family members. However, how gasdermin-mediated pyroptosis is negatively regulated remains unclear. Here, we demonstrate that mannose, a hexose, inhibits GSDME-mediated pyroptosis by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Mechanistically, mannose metabolism in the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway increases levels of the metabolite N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate (GlcNAc-6P), which binds AMPK to facilitate AMPK phosphorylation by LKB1. Activated AMPK then phosphorylates GSDME at Thr6, which leads to blockade of caspase-3-induced GSDME cleavage, thereby repressing pyroptosis. The regulatory role of AMPK-mediated GSDME phosphorylation was further confirmed in AMPK knockout and GSDMET6E or GSDMET6A knock-in mice. In mouse primary cancer models, mannose administration suppressed pyroptosis in small intestine and kidney to alleviate cisplatin- or oxaliplatin-induced tissue toxicity without impairing antitumor effects. The protective effect of mannose was also verified in a small group of patients with gastrointestinal cancer who received normal chemotherapy. Our study reveals a novel mechanism whereby mannose antagonizes GSDME-mediated pyroptosis through GlcNAc-6P-mediated activation of AMPK, and suggests the utility of mannose supplementation in alleviating chemotherapy-induced side effects in clinic applications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41422-023-00848-6
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41422-023-00848-6
Cell Research:《细胞研究》,创刊于1990年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:20.057
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/cr/
投稿链接:https://mts-cr.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
