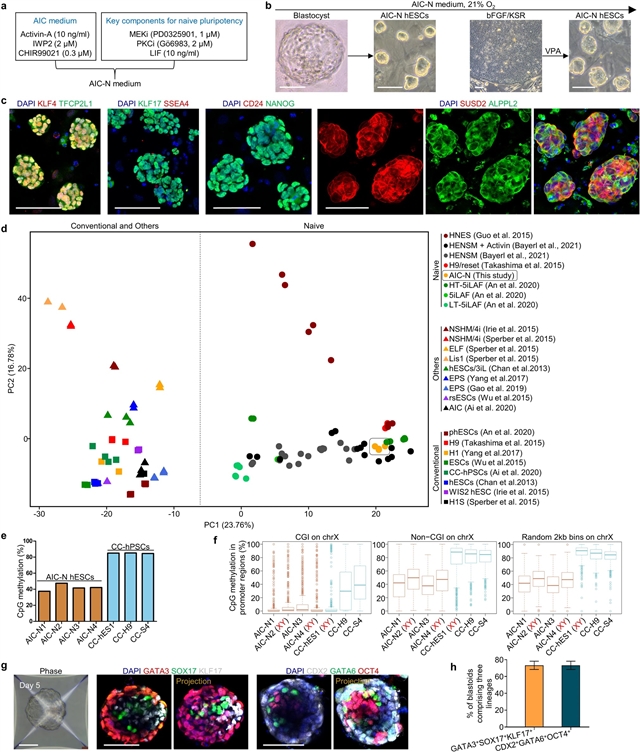
昆明理工大学Tianqing Li、Weizhi Ji和Zongyong Ai合作在研究中取得进展。他们的研究利用培养的人类胚胎和胚胎样类组装体阐明了围着床期的发育特征。2023年7月17日,国际学术期刊《细胞研究》杂志发表了这一成果。
使用3D培养的人类胚胎,研究人员揭示了围着床期早期谱系的完整细胞图谱,并解析了外胚层和次胚层衍生物的细胞组成和基因特征。
此外,研究人员通过对初始hESC和胚胎外细胞进行组装制备了胚胎样组装体(E-assembloid)。使用人类胚胎和胚胎样组装体,研究发现WNT、BMP和Nodal信号通路协同调控人围着床期谱系发育但各自发挥不同的功能。特别是,研究人员解析了胚胎外中胚层和胚胎外内胚层特化的机制。
最后,研究人员制备了一种改进的E-assembloid,其存在原肠胚形成前人类胚胎中具有的外胚层和下胚层发育以及组织结构。该研究结果为人类围着床期发育提供了见解,并且E-assembloid是阐明人类胚胎中细胞行为和信号相互作用十分有用的模型。
研究人员表示,对培养胚胎的研究可为人围着床期的发育特征提供见解。然而,对围着床期谱系发育以及潜在的机制知之甚少。
附:英文原文
Title: Dissecting peri-implantation development using cultured human embryos and embryo-like assembloids
Author: Ai, Zongyong, Niu, Baohua, Yin, Yu, Xiang, Lifeng, Shi, Gaohui, Duan, Kui, Wang, Sile, Hu, Yingjie, Zhang, Chi, Zhang, Chengting, Rong, Lujuan, Kong, Ruize, Chen, Tingwei, Guo, Yixin, Liu, Wanlu, Li, Nan, Zhao, Shumei, Zhu, Xiaoqing, Mai, Xuancheng, Li, Yonggang, Wu, Ze, Zheng, Yi, Fu, Jianping, Ji, Weizhi, Li, Tianqing
Issue&Volume: 2023-07-17
Abstract: Studies of cultured embryos have provided insights into human peri-implantation development. However, detailed knowledge of peri-implantation lineage development as well as underlying mechanisms remains obscure. Using 3D-cultured human embryos, herein we report a complete cell atlas of the early post-implantation lineages and decipher cellular composition and gene signatures of the epiblast and hypoblast derivatives. In addition, we develop an embryo-like assembloid (E-assembloid) by assembling naive hESCs and extraembryonic cells. Using human embryos and E-assembloids, we reveal that WNT, BMP and Nodal signaling pathways synergistically, but functionally differently, orchestrate human peri-implantation lineage development. Specially, we dissect mechanisms underlying extraembryonic mesoderm and extraembryonic endoderm specifications. Finally, an improved E-assembloid is developed to recapitulate the epiblast and hypoblast development and tissue architectures in the pre-gastrulation human embryo. Our findings provide insights into human peri-implantation development, and the E-assembloid offers a useful model to disentangle cellular behaviors and signaling interactions that drive human embryogenesis.
DOI: 10.1038/s41422-023-00846-8
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41422-023-00846-8
Cell Research:《细胞研究》,创刊于1990年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:20.057
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/cr/
投稿链接:https://mts-cr.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
