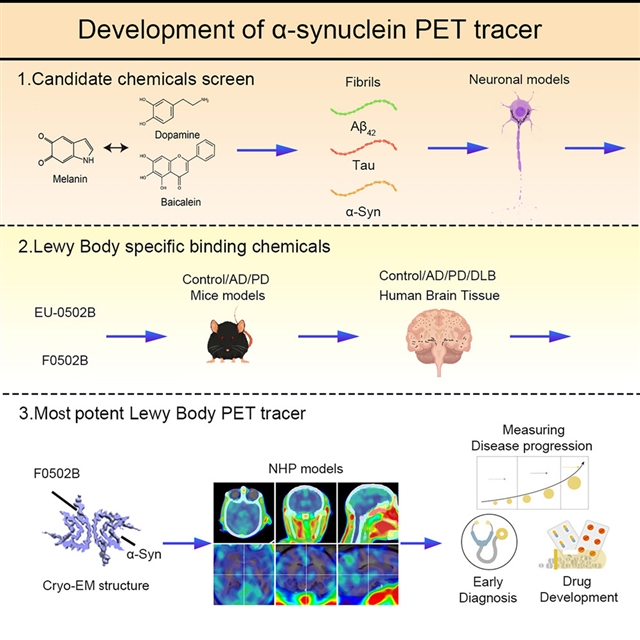
美国埃默里大学医学院Keqiang Ye,上海交通大学Dan Li和武汉大学人民医院Zhentao Zhang共同合作,近期取得重要工作进展。他们研究开发出用于突触核蛋白病成像的α-突触核蛋白正电子发射断层扫描示踪剂。相关研究成果2023年7月7日在线发表于《细胞》杂志上。
据介绍,突触核蛋白病的特征是在大脑中积聚α-突触核蛋白(α-Syn)聚集体。突触核蛋白疾病的正电子发射断层扫描(PET)成像需要选择性结合α-Syn沉积物的放射性药物。
研究人员报道了一种脑可渗透和快速冲洗的PET示踪剂[18F]-F0502B,该示踪剂显示出对α-Syn的高结合亲和力,但对aβ或Tau原纤维没有,并且在脑切片中优先结合α-Syn聚集体。使用来自几种小鼠模型和人类受试者的体外原纤维、神经内聚集物和神经退行性疾病脑切片的几个周期的反筛选,[18F]-F0502B对小鼠和非人灵长类PD模型大脑中的α-Syn沉积进行了成像。研究人员通过冷冻电镜进一步确定了α-Syn原纤维-F0502B复合物的原子结构,并揭示了F0502B通过配体间相互作用形成的强非共价键网络在原纤维表面的平行对角堆积。
总之,这一研究表明,[18F]-F0502B是一种很有前景的先导化合物,可用于对突触核蛋白病中聚集的α-Syn进行成像。
附:英文原文
Title: Development of an α-synuclein positron emission tomography tracer for imaging synucleinopathies
Author: Jie Xiang, Youqi Tao, Yiyuan Xia, Shilin Luo, Qinyue Zhao, Bowei Li, Xiaoqian Zhang, Yunpeng Sun, Wencheng Xia, Mingming Zhang, Seong Su Kang, Eun-Hee Ahn, Xia Liu, Fang Xie, Yihui Guan, Jenny J. Yang, Lihong Bu, Shengxi Wu, Xiaochuan Wang, Xuebing Cao, Cong Liu, Zhentao Zhang, Dan Li, Keqiang Ye
Issue&Volume: 2023-07-07
Abstract: Synucleinopathies are characterized by the accumulation of α-synuclein (α-Syn) aggregatesin the brain. Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of synucleinopathies requiresradiopharmaceuticals that selectively bind α-Syn deposits. We report the identificationof a brain permeable and rapid washout PET tracer [18F]-F0502B, which shows high binding affinity for α-Syn, but not for Aβ or Tau fibrils,and preferential binding to α-Syn aggregates in the brain sections. Employing severalcycles of counter screenings with in vitro fibrils, intraneuronal aggregates, and neurodegenerative disease brain sections fromseveral mice models and human subjects, [18F]-F0502B images α-Syn deposits in the brains of mouse and non-human primate PD models.We further determined the atomic structure of the α-Syn fibril-F0502B complex by cryo-EMand revealed parallel diagonal stacking of F0502B on the fibril surface through anintense noncovalent bonding network via inter-ligand interactions. Therefore, [18F]-F0502B is a promising lead compound for imaging aggregated α-Syn in synucleinopathies.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.06.004
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(23)00644-X
