浙江大学蔡志坚等研究人员合作发现,UBE2M介导的TRIM21 neddylation调节肥胖引起的炎症和代谢紊乱。这一研究成果于2023年6月20日在线发表在国际学术期刊《细胞—代谢》上。
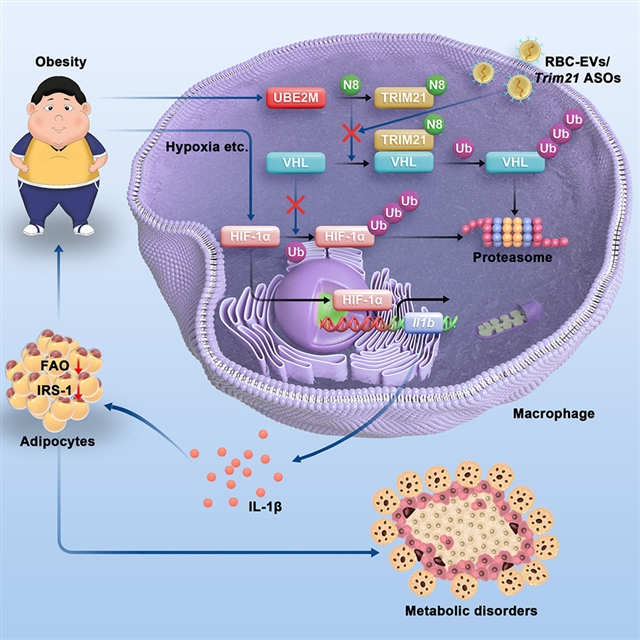
研究人员发现,泛素结合酶E2M(UBE2M)对巨噬细胞诱导的肥胖相关炎症至关重要。在UBE2M缺陷的巨噬细胞的小鼠中,肥胖、胰岛素抵抗和高脂肪饮食诱导的肝脏脂肪变性得到了极大的缓解,这一效果与巨噬细胞因IL-1β产生减少而导致的促炎症活动有关。从机制上讲,UBE2M的缺乏抑制了E3泛素连接酶TRIM21在K129/134上的neddylation,导致E3泛素连接酶VHL的招募和泛素化介导的降解的减少。随后,VHL通过降解HIF-1α来减少HIF-1α诱导的IL-1β产生。用Trim21反义寡核苷酸负载的红血球细胞外囊泡锁定巨噬细胞TRIM21,可有效抑制肥胖引起的炎症和相关的代谢紊乱。因此,这些研究结果表明,巨噬细胞UBE2M对肥胖诱导的炎症至关重要,TRIM21是治疗肥胖和相关代谢疾病的概念验证靶点。
据悉,炎症与肥胖和相关的代谢紊乱密切相关。然而,它在肥胖期间的起源在很大程度上是未知的。
附:英文原文
Title: UBE2M-mediated neddylation of TRIM21 regulates obesity-induced inflammation and metabolic disorders
Author: Xinliang Lu, Xianghui Kong, Hao Wu, Jiayue Hao, Sirui Li, Zichun Gu, Xianchang Zeng, Yingying Shen, Shibo Wang, Jiming Chen, Xuefeng Fei, Yi Sun, Xu Li, Lingling Jiang, Fei Yang, Jianli Wang, Zhijian Cai
Issue&Volume: 2023-06-20
Abstract: Inflammation is closely associated with obesity and related metabolic disorders. However,its origin during obesity is largely unknown. Here, we report that ubiquitin-conjugatingenzyme E2M (UBE2M) is critical to obesity-related inflammation induced by macrophages.In mice with UBE2M-deficient macrophages, obesity, insulin resistance, and hepaticsteatosis induced by a high-fat diet are greatly alleviated, an effect related tothe decreased proinflammatory activity of macrophages due to reduced IL-1β production.Mechanistically, UBE2M deficiency inhibits the neddylation of E3 ubiquitin ligaseTRIM21 on K129/134, leading to reduced recruitment and ubiquitination-mediated degradationof E3 ubiquitin ligase VHL. Subsequently, VHL reduces HIF-1α-induced IL-1β productionby degrading HIF-1α. Targeting macrophage TRIM21 with Trim21 antisense oligonucleotide-loaded red blood cell extracellular vesicles effectivelyinhibits obesity-induced inflammation and related metabolic disorders. Thus, our resultsdemonstrate that macrophage UBE2M is essential for obesity-induced inflammation andthat TRIM21 is a proof-of-concept target for treating obesity and associated metabolicdiseases.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.05.011
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(23)00209-7
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
