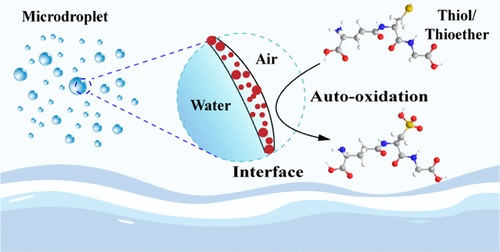
溶解的有机硫,包括硫醇和硫醚,通过海洋飞沫气溶胶(SSA)从海洋表面输送到大气,对全球硫循环具有重要意义。SSA中的硫醇/硫醚发生快速氧化,这在历程上与光化学过程有关。
该文中,研究人员报道了在SSA中发现的硫醇/硫醚氧化的非光化学自发途径。在研究的10种天然丰富的硫醇/硫醚中,有7种在SSA中表现出快速氧化,其中二硫化物、亚砜和砜是主要产物。研究人员认为,硫醇/硫醚的这种自发氧化主要是由硫醇/硫乙醚在空气-水界面的富集,和通过在水微滴表面或附近的离子(例如,脱质子化谷胱甘肽电离产生的谷胱甘肽自由基)失去电子而产生的高活性自由基推动的。
该工作揭示了一种普遍存在但以前被忽视的硫醇/硫醚氧化途径,可能有助于加速硫循环以及海洋-大气界面的相关金属转化(如汞)。
附:英文原文
Title: Spontaneous Oxidation of Thiols and Thioether at the Air–Water Interface of a Sea Spray Microdroplet
Author: Zepeng Rao, Xiaojiao Li, Ye-Guang Fang, Joseph S. Francisco, Chongqin Zhu, Chiheng Chu
Issue&Volume: May 3, 2023
Abstract: The transport of dissolved organic sulfur, including thiols and thioethers, from the ocean surface to the atmosphere through sea spray aerosol (SSA) is of great importance for the global sulfur cycle. Thiol/thioether in SSA undergoes rapid oxidation that is historically linked to photochemical processes. Here, we report the discovery of a non-photochemical, spontaneous path of thiol/thioether oxidation in SSA. Among 10 investigated naturally abundant thiol/thioether, seven species displayed rapid oxidation in SSA, with disulfide, sulfoxide, and sulfone comprising the major products. We suggest that such spontaneous oxidation of thiol/thioether was mainly fueled by thiol/thioether enrichment at the air–water interface and generation of highly reactive radicals by the loss of an electron from ions (e.g., glutathionyl radical produced from ionization of deprotonated glutathione) at or near the surface of the water microdroplet. Our work sheds light on a ubiquitous but previously overlooked pathway of thiol/thioether oxidation, which could contribute to an accelerated sulfur cycle as well as related metal transformation (e.g., mercury) at ocean–atmosphere interfaces.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c02334
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.3c02334
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
