美国华盛顿大学医学院Evan E. Eichler小组揭示人类片段重复内的突变和基因转换增加。这一研究成果于2023年5月10日发表在国际学术期刊《自然》上。
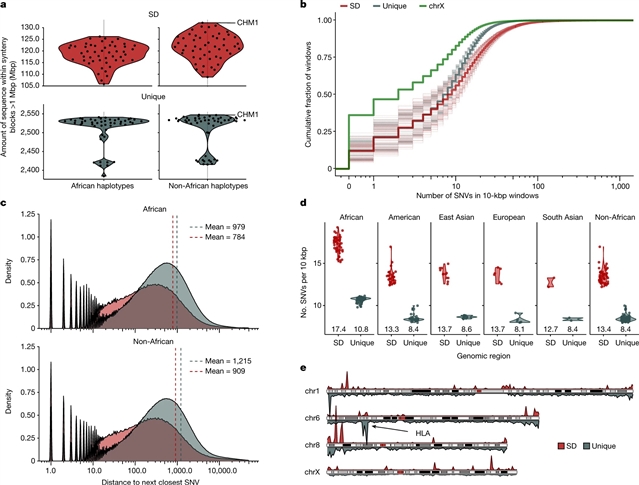
研究人员构建了1:1的无歧义排列,横跨102个人类单倍型的高同一性片段重复(SD),并比较了独特和重复区域之间的单核苷酸变异(SNV)模式。研究人员发现,与独特区域相比,人类的SNV在SD中增加了60%,并且估计这一增加至少有23%是由于焦点间基因转换(IGC)造成的,每个人类单倍型平均有多达4.3兆字节的SD序列转换。研究人员开发了一个全基因组的IGC供体和受体图,包括498个受体和454个供体热点,影响到大约800个蛋白质编码基因的外显子。这些包括171个基因,它们在人类单倍型的一个子集中平均“迁移”了1.61兆字节对。
使用凝聚框架,研究人员表明,与独特的序列相比,SD区域在进化上略显古老,这可能是由于IGC。然而,SD中的SNV显示了一个独特的突变谱:在所有三联体背景下,将胞嘧啶转化为鸟嘌呤或相反的转化增加了27.1%,与独特DNA相比,CpG相关突变的频率减少了7.6%。研究人员认为,这些不同的突变特性有助于保持SD DNA总体上比独特DNA更高的GC含量,这可能是由同族序列之间的GC偏向转换所驱动的。
据了解,由于短读测序数据映射的局限性,SD中的SNV还没有得到系统的评估。
附:英文原文
Title: Increased mutation and gene conversion within human segmental duplications
Author: Vollger, Mitchell R., Dishuck, Philip C., Harvey, William T., DeWitt, William S., Guitart, Xavi, Goldberg, Michael E., Rozanski, Allison N., Lucas, Julian, Asri, Mobin, Munson, Katherine M., Lewis, Alexandra P., Hoekzema, Kendra, Logsdon, Glennis A., Porubsky, David, Paten, Benedict, Harris, Kelley, Hsieh, PingHsun, Eichler, Evan E.
Issue&Volume: 2023-05-10
Abstract: Single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) in segmental duplications (SDs) have not been systematically assessed because of the limitations of mapping short-read sequencing data1,2. Here we constructed 1:1 unambiguous alignments spanning high-identity SDs across 102 human haplotypes and compared the pattern of SNVs between unique and duplicated regions3,4. We find that human SNVs are elevated 60% in SDs compared to unique regions and estimate that at least 23% of this increase is due to interlocus gene conversion (IGC) with up to 4.3megabase pairs of SD sequence converted on average per human haplotype. We develop a genome-wide map of IGC donors and acceptors, including 498 acceptor and 454 donor hotspots affecting the exons of about 800 protein-coding genes. These include 171 genes that have ‘relocated’ on average 1.61megabase pairs in a subset of human haplotypes. Using a coalescent framework, we show that SD regions are slightly evolutionarily older when compared to unique sequences, probably owing to IGC. SNVs in SDs, however, show a distinct mutational spectrum: a 27.1% increase in transversions that convert cytosine to guanine or the reverse across all triplet contexts and a 7.6% reduction in the frequency of CpG-associated mutations when compared to unique DNA. We reason that these distinct mutational properties help to maintain an overall higher GC content of SD DNA compared to that of unique DNA, probably driven by GC-biased conversion between paralogous sequences5,6.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-05895-y
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-05895-y
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
