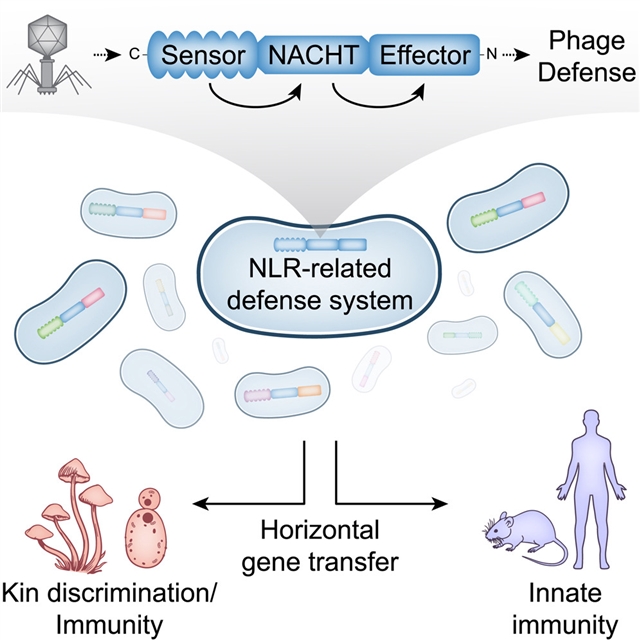
美国科罗拉多大学Aaron T. Whiteley课题组发现,细菌的NLR相关蛋白可防止噬菌体入侵。该项研究成果于2023年5月8日在线发表在《细胞》杂志上。
研究人员展示了含有NACHT模块的蛋白质,这是动物核苷酸结合域和富含亮氨酸重复基因家族(NLR)的核心特征,其在细菌中被发现并防御噬菌体。NACHT蛋白广泛存在于细菌中,对DNA和RNA噬菌体提供免疫力,并显示出C端传感器、中间NACHT和N端效应器模块的特征。一些细菌NACHT蛋白具有与人类NLR相似的结构域,是炎症体的关键成分。人类疾病相关的NLR突变导致炎症小体不依赖刺激的激活,也会激活细菌NACHT蛋白,从而支持一种共享的信号传导机制。这项工作确定了含有NACHT模块的蛋白是整个生命树上先天免疫的古老媒介。
据介绍,细菌使用广泛的免疫途径来对抗噬菌体感染。这些基因的一个亚群与真核生物免疫系统的成分有同源性,这表明真核生物从细菌那里横向获得了某些先天免疫基因。
附:英文原文
Title: Bacterial NLR-related proteins protect against phage
Author: Emily M. Kibby, Amy N. Conte, A. Maxwell Burroughs, Toni A. Nagy, Jose A. Vargas, Lindsay A. Whalen, L. Aravind, Aaron T. Whiteley
Issue&Volume: 2023-05-08
Abstract: Bacteria use a wide range of immune pathways to counter phage infection. A subsetof these genes shares homology with components of eukaryotic immune systems, suggestingthat eukaryotes horizontally acquired certain innate immune genes from bacteria. Here,we show that proteins containing a NACHT module, the central feature of the animalnucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat containing gene family (NLRs), arefound in bacteria and defend against phages. NACHT proteins are widespread in bacteria,provide immunity against both DNA and RNA phages, and display the characteristic C-terminalsensor, central NACHT, and N-terminal effector modules. Some bacterial NACHT proteinshave domain architectures similar to the human NLRs that are critical components ofinflammasomes. Human disease-associated NLR mutations that cause stimulus-independentactivation of the inflammasome also activate bacterial NACHT proteins, supportinga shared signaling mechanism. This work establishes that NACHT module-containing proteinsare ancient mediators of innate immunity across the tree of life.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.04.015
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(23)00411-7
