美国耶鲁大学Mark Gerstein等研究人员合作报道多组织个人表观基因组和变异影响模型的EN-Ex资源。相关论文于2023年3月30日发表在《细胞》杂志上。
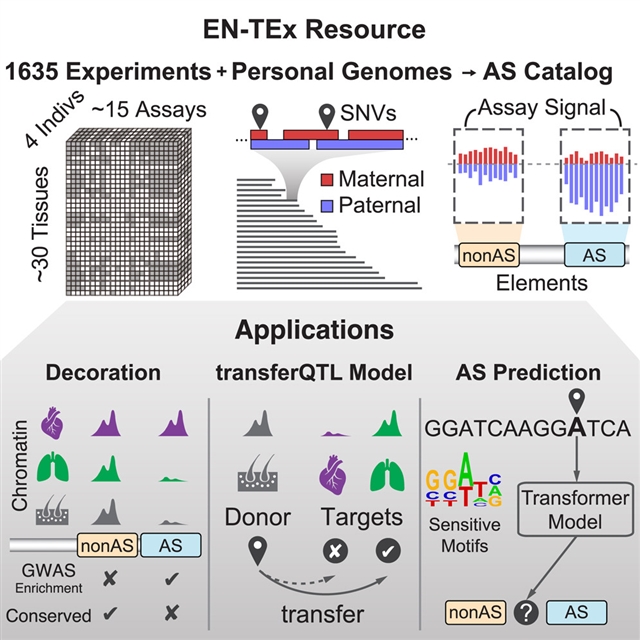
研究人员提出了EN-Ex资源,包括来自四个捐赠者的1635个开放性数据集(30个组织×15个检测)。这些数据集被映射到匹配的二倍体基因组上,具有长读相位和结构变异,实例化了超过100万个等位基因特异性位点的目录。这些基因座沿着单倍型表现出协调的活动,并且比相应的、非等位基因特异性的基因座保守得少。令人惊讶的是,一个深度学习的转化器模型可以仅根据局部的核苷酸序列背景来预测等位基因的特异性活动,突出了转录因子结合模体的重要性,尤其是对变异体敏感。
此外,将EN-Ex与现有的基因组注释相结合,研究人员揭示了等位基因特异性和GWAS位点之间的强烈关联。它还能将已知的eQTL转移到难以描述的组织(如从皮肤到心脏)的模型。总的来说,EN-Ex为更准确的个人功能基因组学提供了丰富的数据和可推广的模型。
据悉,了解遗传变异如何影响分子表型是功能基因组学的一个关键目标,目前由于依赖单一的单倍体参考基因组而受到阻碍。
附:英文原文
Title: The EN-TEx resource of multi-tissue personal epigenomes & variant-impact models
Author: Joel Rozowsky, Jiahao Gao, Beatrice Borsari, Yucheng T. Yang, Timur Galeev, Gamze Gürsoy, Charles B. Epstein, Kun Xiong, Jinrui Xu, Tianxiao Li, Jason Liu, Keyang Yu, Ana Berthel, Zhanlin Chen, Fabio Navarro, Maxwell S. Sun, James Wright, Justin Chang, Christopher J.F. Cameron, Noam Shoresh, Elizabeth Gaskell, Jorg Drenkow, Jessika Adrian, Sergey Aganezov, Franois Aguet, Gabriela Balderrama-Gutierrez, Samridhi Banskota, Guillermo Barreto Corona, Sora Chee, Surya B. Chhetri, Gabriel Conte Cortez Martins, Cassidy Danyko, Carrie A. Davis, Daniel Farid, Nina P. Farrell, Idan Gabdank, Yoel Gofin, David U. Gorkin, Mengting Gu, Vivian Hecht, Benjamin C. Hitz, Robbyn Issner, Yunzhe Jiang, Melanie Kirsche, Xiangmeng Kong, Bonita R. Lam, Shantao Li, Bian Li, Xiqi Li, Khine Zin Lin, Ruibang Luo, Mark Mackiewicz, Ran Meng, Jill E. Moore, Jonathan Mudge, Nicholas Nelson, Chad Nusbaum, Ioann Popov, Henry E. Pratt, Yunjiang Qiu, Srividya Ramakrishnan, Joe Raymond
Issue&Volume: 2023/03/30
Abstract: Understanding how genetic variants impact molecular phenotypes is a key goal of functional genomics, currently hindered by reliance on a single haploid reference genome. Here, we present the EN-TEx resource of 1,635 open-access datasets from four donors (~30 tissues × ~15 assays). The datasets are mapped to matched, diploid genomes with long-read phasing and structural variants, instantiating a catalog of >1 million allele-specific loci. These loci exhibit coordinated activity along haplotypes and are less conserved than corresponding, non-allele-specific ones. Surprisingly, a deep-learning transformer model can predict the allele-specific activity based only on local nucleotide-sequence context, highlighting the importance of transcription-factor-binding motifs particularly sensitive to variants. Furthermore, combining EN-TEx with existing genome annotations reveals strong associations between allele-specific and GWAS loci. It also enables models for transferring known eQTLs to difficult-to-profile tissues (e.g., from skin to heart). Overall, EN-TEx provides rich data and generalizable models for more accurate personal functional genomics.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.02.018
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(23)00161-7
