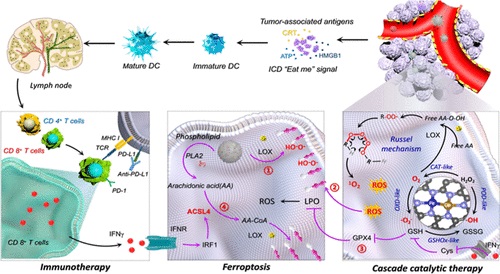
免疫治疗是目前最有前途的长期肿瘤消退治疗策略。然而,由于肿瘤细胞的免疫原性不足,目前的癌症免疫治疗显示出较低的应答率。
该文中,研究人员报道了一种通过触发级联免疫原性肿瘤脱铁性来保持肿瘤细胞高度免疫原性的策略。研究人员开发了一种六酶共表达的纳米平台:脂氧合酶(LOX)和磷脂酶A2(PLA2)-共负载的FeCo/Fe–co双金属原子纳米酶(FeCo/Fe-co DAzyme/PL),其不仅可以通过自身的多酶模拟活性诱导初始免疫原性肿瘤脱铁,而且可以上调花生四烯酸(AA)的表达,与CD8+T细胞衍生的IFN-γ协同诱导ACSL4介导的免疫原性瘤脱铁。在这个过程中,FeCo/Fe–Co DAzyme/PL可以通过有效地产生活性氧(ROS)并消耗肿瘤部位的GSH和GPX4来诱导脂质过氧化(LPO)。
此外,在IFN-γ刺激的ACSL4激活下,PLA2催化释放的游离AA转化为花生四烯酸,ACSL4进一步结合到膜上的磷脂中,并在LOX的参与下过氧化。因此,FeCo/Fe–Co DAzyme/PL可以通过多种ROS风暴、GSH/GPX4耗竭、LOX催化和IFN-γ介导的ACSL4激活来促进不可逆的级联免疫原性脱铁,构建了一条克服当前免疫疗法缺点的有效途径。
附:英文原文
Title: Multi-enzyme Co-expressed Dual-Atom Nanozymes Induce Cascade Immunogenic Ferroptosis via Activating Interferon-γ and Targeting Arachidonic Acid Metabolism
Author: Yang Liu, Rui Niu, Ruiping Deng, Shuyan Song, Yinghui Wang, Hongjie Zhang
Issue&Volume: April 14, 2023
Abstract: Immunotherapy is currently the most promising treatment strategy for long-term tumor regression. However, current cancer immunotherapy shows low response rates due to insufficient immunogenicity of tumor cells. Herein, we report a strategy to keep tumor cells highly immunogenic by triggering cascade immunogenic tumor ferroptosis. We developed a six-enzyme co-expressed nanoplatform: lipoxygenase (LOX) and phospholipase A2 (PLA2)-co-loaded FeCo/Fe–Co dual-metal atom nanozyme (FeCo/Fe–Co DAzyme/PL), which can not only induce initial immunogenic tumor ferroptosis through its own multi-enzyme mimetic activities but also up-regulate arachidonic acid (AA) expression to synergize with CD8+ T cell-derived IFN-γ to induce ACSL4-mediated immunogenic tumor ferroptosis. During this process, FeCo/Fe–Co DAzyme/PL can induce lipid peroxidation (LPO) by efficiently generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) and depleting GSH and GPX4 at tumor sites. Additionally, free AA released from PLA2 catalysis is converted into arachidonyl-CoA under the activation of ACSL4 stimulated by IFN-γ, which is further incorporated into phospholipids on membranes and peroxidized with the participation of LOX. Consequently, FeCo/Fe–Co DAzyme/PL can promote irreversible cascade immunogenic ferroptosis through multiple ROS storms, GSH/GPX4 depletion, LOX catalysis, and IFN-γ-mediated ACSL4 activation, constructing an effective pathway to overcome the drawbacks of current immunotherapy.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c13689
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.2c13689
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
