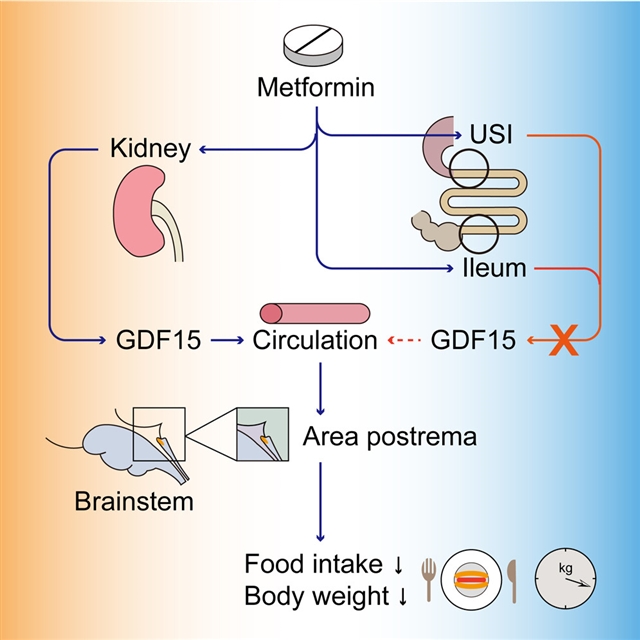
加拿大多伦多综合医院研究所Tony K.T. Lam团队发现,二甲双胍引发肾脏GDF15依赖的最后区轴来调节食物摄入和体重。2023年4月14日,《细胞—代谢》杂志在线发表了这项成果。
研究人员表示,二甲双胍是治疗肥胖相关的2型糖尿病(T2D)最广泛的处方药,它能降低啮齿动物和人类的血浆葡萄糖水平、食物摄入量和体重,但其作用的机理部位仍然难以确定。二甲双胍增加血浆生长/分化因子15(GDF15)的水平来调节能量平衡,而GDF15的施用激活了在最后区(AP)和后脑孤束核(NTS)高度表达的GDNF家族受体α样(GFRAL)来降低食物摄入和体重。然而,二甲双胍治疗后血浆GDF15水平的组织特异性贡献仍有争议。
研究人员发现二甲双胍通过上调肾脏的GDF15合成,增加了高脂肪(HF)喂养的雄性大鼠的血浆GDF15水平。重要的是,肾脏特异性敲除GDF15的表达以及AP特异性敲除GFRAL的表达,否定了二甲双胍降低食物摄入和体重增加的能力。总之,这些发现揭示了肾脏是二甲双胍通过肾脏GDF15依赖的AP轴调节能量平衡的一个靶点。
附:英文原文
Title: Metformin triggers a kidney GDF15-dependent area postrema axis to regulate food intake and body weight
Author: Song-Yang Zhang, Kyla Bruce, Zahra Danaei, Rosa J.W. Li, Daniel R. Barros, Rachel Kuah, Yu-Mi Lim, Laura H. Mariani, David Z. Cherney, Jennifer F.M. Chiu, Heather N. Reich, Tony K.T. Lam
Issue&Volume: 2023-04-14
Abstract: Metformin, the most widely prescribed medication for obesity-associated type 2 diabetes(T2D), lowers plasma glucose levels, food intake, and body weight in rodents and humans,but the mechanistic site(s) of action remain elusive. Metformin increases plasma growth/differentiationfactor 15 (GDF15) levels to regulate energy balance, while GDF15 administration activatesGDNF family receptor α-like (GFRAL) that is highly expressed in the area postrema(AP) and the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) of the hindbrain to lower food intakeand body weight. However, the tissue-specific contribution of plasma GDF15 levelsafter metformin treatment is still under debate. Here, we found that metformin increasedplasma GDF15 levels in high-fat (HF) fed male rats through the upregulation of GDF15synthesis in the kidney. Importantly, the kidney-specific knockdown of GDF15 expressionas well as the AP-specific knockdown of GFRAL expression negated the ability of metforminto lower food intake and body weight gain. Taken together, we unveil the kidney asa target of metformin to regulate energy homeostasis through a kidney GDF15-dependentAP axis.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.03.014
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(23)00092-X
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
