近日,美国莱斯大学仪鸣教授课题组与劳伦斯伯克利国家实验室的Robert J.Birgeneau教授等人合作,研究了kagome FeGe中的磁性和电荷密度波序。相关成果已于2023年3月13日在国际学术期刊《自然—物理学》上发表。
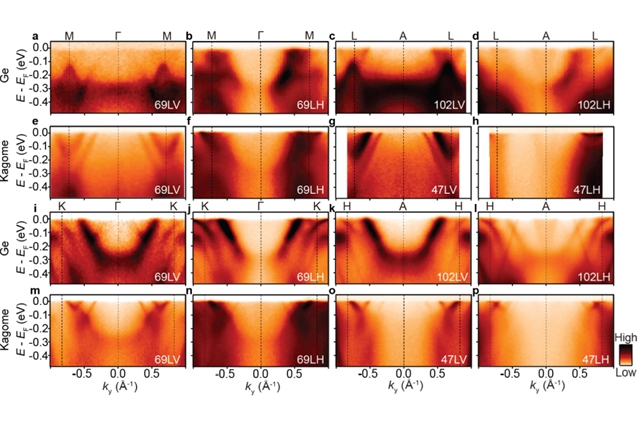
该研究团队使用角分辨光电发射光谱观察了FeGe中kagome晶格的三个电子特征。费米能级附近的范霍夫(van Hove)奇点的存在是由基础磁性交换分裂所驱动的。此外,他们还展示了电荷密度波的光谱证据,即费米能级附近的能隙。他们的观察结果表明,磁相互作用驱动的能带修正导致电荷密度波的形成,并指出这种中度相关的kagome金属中新兴磁性和电荷顺序之间存在交织的联系。
据悉,电子相关性经常导致量子材料中的演生顺序,其中一个例子是kagome晶格材料,在电子之间存在强关联时,具有拓扑态。这源于与kagome晶格几何相关的电子能带结构的特征:由电子波函数的破坏性干涉引起的平带、拓扑Dirac交叉和一对范霍夫奇点。人们在kagome晶格材料中发现了各种相关的电子相,包括磁性、电荷密度波、向列性和超导性。最近,在磁性kagome FeGe中发现了电荷密度波,为理解kagome材料中电荷顺序与磁性之间的相互作用提供了平台。
附:英文原文
Title: Magnetism and charge density wave order in kagome FeGe
Author: Teng, Xiaokun, Oh, Ji Seop, Tan, Hengxin, Chen, Lebing, Huang, Jianwei, Gao, Bin, Yin, Jia-Xin, Chu, Jiun-Haw, Hashimoto, Makoto, Lu, Donghui, Jozwiak, Chris, Bostwick, Aaron, Rotenberg, Eli, Granroth, Garrett E., Yan, Binghai, Birgeneau, Robert J., Dai, Pengcheng, Yi, Ming
Issue&Volume: 2023-03-13
Abstract: Electron correlations often lead to emergent orders in quantum materials, and one example is the kagome lattice materials where topological states exist in the presence of strong correlations between electrons. This arises from the features of the electronic band structure that are associated with the kagome lattice geometry: flat bands induced by destructive interference of the electronic wavefunctions, topological Dirac crossings and a pair of van Hove singularities. Various correlated electronic phases have been discovered in kagome lattice materials, including magnetism, charge density waves, nematicity and superconductivity. Recently, a charge density wave was discovered in the magnetic kagome FeGe, providing a platform for understanding the interplay between charge order and magnetism in kagome materials. Here we observe all three electronic signatures of the kagome lattice in FeGe using angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. The presence of van Hove singularities near the Fermi level is driven by the underlying magnetic exchange splitting. Furthermore, we show spectral evidence for the charge density wave as gaps near the Fermi level. Our observations point to the magnetic interaction-driven band modification resulting in the formation of the charge density wave and indicate an intertwined connection between the emergent magnetism and charge order in this moderately correlated kagome metal.
DOI: 10.1038/s41567-023-01985-w
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-023-01985-w
