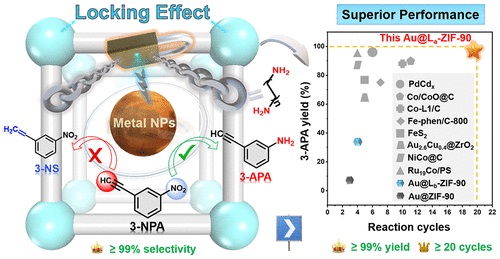
超小金属纳米颗粒(NPs)在多相催化中表现出高催化活性,但在催化过程中容易团聚和损失,导致化学选择性低和效率低。
该文中,研究人员提出了一种锁定效应策略,以在金属-有机框架(MOFs)中合成高负载和超细金属NPs,以实现高稳定性的高效化学选择性催化。简言之,具有醛基的MOF ZIF-90通过醛亚胺缩合与二胺链协同作用,被用于限制Au NPs的原位形成,表示为Au@L-ZIF-90。优化的Au@La-ZIF-90具有高度分散的Au NPs(2.60±0.81nm),负载量约为22wt%,并且通过3-硝基苯基乙炔(3-NPA)的选择性氢化对3-氨基苯乙炔(3-APA)表现出优异的性能,具有高收率(99%)和优异的耐久性(超过20个循环),远远优于没有锁链的对比催化剂和其他报道的催化剂。
实验表征和系统密度泛函理论计算进一步表明,锁定MOFs调节Au纳米颗粒的电荷,使其对硝基氢化具有高度特异性,以获得具有高选择性(99%)的3-APA。此外,这种锁定效应策略也适用于限制在多种MOF中的其他金属纳米颗粒,所有这些与链锁定的催化剂都显示出获得3-APA的极大选择性(≥90%)。
该项工作中提出的策略提供了一种新的通用的方法,用于精确控制具有可编程MOF微环境的可接近金属纳米颗粒的固有活性,以实现高度特异性催化。
附:英文原文
Title:Locking Effect in Metal@MOF with Superior Stability for Highly Chemoselective Catalysis
Author: Yicheng Zhong, Peisen Liao, Jiawei Kang, Qinglin Liu, Shihan Wang, Suisheng Li, Xianlong Liu, Guangqin Li
Issue&Volume: February 15, 2023
Abstract: Ultrasmall metal nanoparticles (NPs) show high catalytic activity in heterogeneous catalysis but are prone to reunion and loss during the catalytic process, resulting in low chemoselectivity and poor efficiency. Herein, a locking effect strategy is proposed to synthesize high-loading and ultrafine metal NPs in metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) for efficient chemoselective catalysis with high stability. Briefly, the MOF ZIF-90 with aldehyde groups cooperating with diamine chains via aldimine condensation was interlocked, which was employed to confine in situ formation of Au NPs, denoted as Au@L-ZIF-90. The optimized Au@La-ZIF-90 has highly dispersed Au NPs (2.60 ± 0.81 nm) with a loading amount around 22 wt % and shows a great performance toward 3-aminophenylacetylene (3-APA) from the selective hydrogenation of 3-nitrophenylacetylene (3-NPA) with a high yield (99%) and excellent durability (over 20 cycles), far superior to contrast catalysts without chains locking and other reported catalysts. In addition, experimental characterization and systematic density functional theory calculations further demonstrate that the locked MOF modulates the charge of Au nanoparticles, making them highly specific for nitro group hydrogenation to obtain 3-APA with high selectivity (99%). Furthermore, this locking effect strategy is also applicable to other metal nanoparticles confined in a variety of MOFs, and all of these catalysts locked with chains show great selectivity (≥90%) of 3-APA. The proposed strategy in this work provides a novel and universal method for precise control of the inherent activity of accessible metal nanoparticles with a programmable MOF microenvironment toward highly specific catalysis.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c12590
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.2c12590
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
