复旦大学周鸣飞团队报道了苯甲醛-(H2O) 1-6团簇中溶质-水相互作用的演化
对气相溶质-水团簇的优选排列和分子间相互作用的研究揭示了控制水溶液结构和动力学的分子间势。
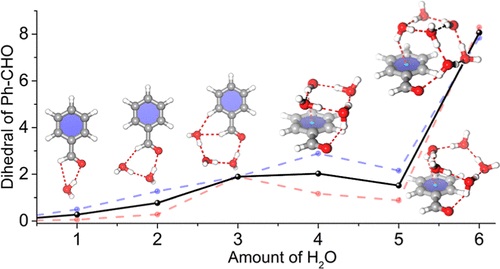
该文中,研究人员报道了使用宽带旋转光谱在脉冲超声速膨胀中对苯甲醛-(水)n(n=1–6)团簇水合配位网络的研究。苯甲醛(PhCHO)是最简单的芳香醛,它包含亲水性(CHO)和疏水性(苯环)官能团,可以模拟具有生物学意义的分子。对于n=1–3簇,水分子通过强CO···HO氢键和弱CH···OH氢键连接在苯甲醛的亲水CHO部分周围。对于较大的簇,其光谱与聚类化合物在PhCHO表面的配位结构一致,亲水性CHO和疏水性苯环基团都参与了键合相互作用。苯甲醛的存在不会强烈干扰环状水四聚体和五聚体,它们保持与纯水簇中相同的结构。
水六聚体的书状异构体而不是笼状或棱柱状异构体被合并到微溶团簇中。顺序加入水分子后,PhCHO分子偏离平面结构。PhCHO–(H2O)1–6簇可以作为理解水环境中生物相关分子的溶质-水相互作用的简单模型系统。
附:英文原文
Title: Evolution of Solute–Water Interactions in the Benzaldehyde-(H2O)1–6 Clusters by Rotational Spectroscopy
Author: Weixing Li, Cristóbal Pérez, Amanda L. Steber, Melanie Schnell, Dingding Lv, Guanjun Wang, Xiaoqing Zeng, Mingfei Zhou
Issue&Volume: February 10, 2023
Abstract: The investigation on the preferred arrangement and intermolecular interactions of gas phase solute–water clusters gives insights into the intermolecular potentials that govern the structure and dynamics of the aqueous solutions. Here, we report the investigation of hydrated coordination networks of benzaldehyde-(water)n (n = 1–6) clusters in a pulsed supersonic expansion using broadband rotational spectroscopy. Benzaldehyde (PhCHO) is the simplest aromatic aldehyde that involves both hydrophilic (CHO) and hydrophobic (phenyl ring) functional groups, which can mimic molecules of biological significance. For the n = 1–3 clusters, the water molecules are connected around the hydrophilic CHO moiety of benzaldehyde through a strong CO···HO hydrogen bond and weak CH···OH hydrogen bond(s). For the larger clusters, the spectra are consistent with the structures in which the water clusters are coordinated on the surface of PhCHO with both the hydrophilic CHO and hydrophobic phenyl ring groups being involved in the bonding interactions. The presence of benzaldehyde does not strongly interfere with the cyclic water tetramer and pentamer, which retain the same structure as in the pure water cluster. The book isomer instead of cage or prism isomers of the water hexamer is incorporated into the microsolvated cluster. The PhCHO molecule deviates from the planar structure upon sequential addition of water molecules. The PhCHO–(H2O)1–6 clusters may serve as a simple model system in understanding the solute–water interactions of biologically relevant molecules in an aqueous environment.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c11732
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.2c11732
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
