美国加州大学Yang Peidong团队使用Operando技术揭示用于CO2电还原的活性铜纳米颗粒。相关研究成果于2023年2月8日发表在《自然》。
二电还原氧化碳有助于燃料和化学品的可持续合成。尽管Cu能够使CO2转化为多碳产物(C2+),但在操作条件下活性位点的性质仍然难以确定。重要的是,鉴定高性能铜纳米催化剂的活性位点需要纳米级的时间分辨操作技术。
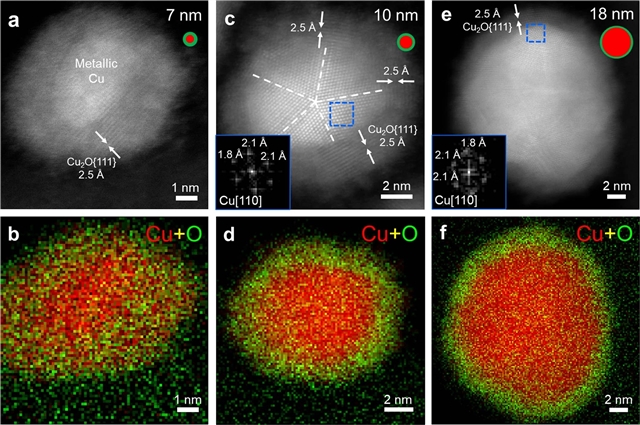
该文中,研究人员对铜纳米催化剂生命周期中的结构动力学进行了全面的研究。在电解过程中,7nm Cu纳米颗粒整体演变成金属Cu纳米颗粒,然后在电解后空气暴露后完全氧化成单晶Cu2O纳米立方体。Operando分析和四维电化学液体电池扫描透射电子显微镜显示,在CO2还原条件下存在金属Cu纳米颗粒。相关的高能量分辨率时间分辨X射线光谱表明,富含纳米晶界的金属Cu支持C–C耦合的欠协调活性位点。
定量结构-活性相关性表明,较高比例的金属Cu纳米颗粒导致较高的C2+选择性。一个7nm的Cu纳米颗粒集合体,具有一个单位分数的活性Cu纳米颗粒,显示出比具有三分之一活性Cu纳米晶粒的18nm对应物高六倍的C2+选择性。多峰操作技术的相关性为人们深入了解电化学条件下纳米催化剂的复杂结构演变提供了一个强大的平台。
附:英文原文
Title: Operando studies reveal active Cu nanograins for CO2 electroreduction
Author: Yang, Yao, Louisia, Sheena, Yu, Sunmoon, Jin, Jianbo, Roh, Inwhan, Chen, Chubai, Fonseca Guzman, Maria V., Feijo, Julian, Chen, Peng-Cheng, Wang, Hongsen, Pollock, Christopher J., Huang, Xin, Shao, Yu-Tsun, Wang, Cheng, Muller, David A., Abrua, Hctor D., Yang, Peidong
Issue&Volume: 2023-02-08
Abstract: Carbon dioxide electroreduction facilitates the sustainable synthesis of fuels and chemicals1. Although Cu enables CO2-to-multicarbon product (C2+) conversion, the nature of the active sites under operating conditions remains elusive2. Importantly, identifying active sites of high-performance Cu nanocatalysts necessitates nanoscale, time-resolved operando techniques3,4,5. Here, we present a comprehensive investigation of the structural dynamics during the life cycle of Cu nanocatalysts. A 7nm Cu nanoparticle ensemble evolves into metallic Cu nanograins during electrolysis before complete oxidation to single-crystal Cu2O nanocubes following post-electrolysis air exposure. Operando analytical and four-dimensional electrochemical liquid-cell scanning transmission electron microscopy shows the presence of metallic Cu nanograins under CO2 reduction conditions. Correlated high-energy-resolution time-resolved X-ray spectroscopy suggests that metallic Cu, rich in nanograin boundaries, supports undercoordinated active sites for C–C coupling. Quantitative structure–activity correlation shows that a higher fraction of metallic Cu nanograins leads to higher C2+ selectivity. A 7nm Cu nanoparticle ensemble, with a unity fraction of active Cu nanograins, exhibits sixfold higher C2+ selectivity than the 18nm counterpart with one-third of active Cu nanograins. The correlation of multimodal operando techniques serves as a powerful platform to advance our fundamental understanding of the complex structural evolution of nanocatalysts under electrochemical conditions.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05540-0
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-05540-0
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
