美国马里兰大学教授Wang, Chunsheng团队报道了极端工作条件下锂离子电池的电解液设计。相关研究成果于2023年2月8日发表于国际一流学术期刊《自然》。
广泛使用的LiNi0.8Mn0.1Co0.1O2(NMC811)||石墨锂离子电池的理想电解液需要具有支持更高电压(≥4.5伏)、快速充电(≤15分钟)、在宽温度范围(±60摄氏度)内充电/放电而不需要锂镀层以及不燃性的能力。没有一种现有的电解质同时满足所有这些要求,电解质设计因缺乏有效的指导原则而受到阻碍,该原则解决了电池性能、溶剂化结构和固体电解质界面化学之间的关系。
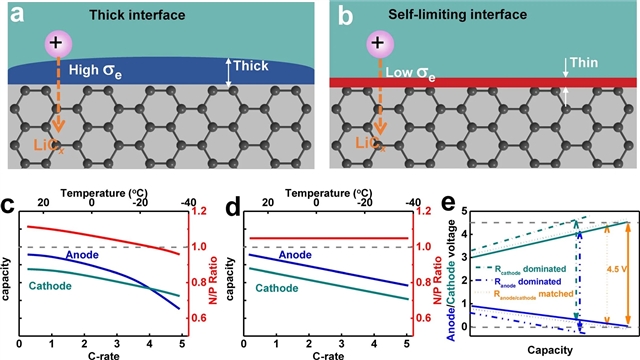
该文中,研究人员报告并验证了基于一组软溶剂的电解质设计策略,该策略在弱Li+-溶剂相互作用、充分的盐解离和期望的电化学之间取得平衡,以满足所有上述要求。值得注意的是,当这些电池在50摄氏度(60摄氏度)下以0.1C的C速率充放电时,面积容量超过2.5mAh/cm2的4.5伏NMC811石墨袋状电池保持其室温容量的75%(54%),具有贫电解质(2.5g/Ah)的NMC811石墨袋电池在30摄氏度下实现了稳定的循环,平均库仑效率超过99.9%。综合分析进一步揭示了NMC811阴极和石墨阳极之间的阻抗匹配,这是由于形成了类似的富氟化锂界面,从而有效避免了低温下的锂电镀。
该电解质设计原理可以扩展到在极端条件下运行的其他碱金属离子电池。
附:英文原文
Title: Electrolyte design for Li-ion batteries under extreme operating conditions
Author: Xu, Jijian, Zhang, Jiaxun, Pollard, Travis P., Li, Qingdong, Tan, Sha, Hou, Singyuk, Wan, Hongli, Chen, Fu, He, Huixin, Hu, Enyuan, Xu, Kang, Yang, Xiao-Qing, Borodin, Oleg, Wang, Chunsheng
Issue&Volume: 2023-02-08
Abstract: The ideal electrolyte for the widely used LiNi0.8Mn0.1Co0.1O2 (NMC811)||graphite lithium-ion batteries is expected to have the capability of supporting higher voltages (≥4.5volts), fast charging (≤15minutes), charging/discharging over a wide temperature range (±60degrees Celsius) without lithium plating, and non-flammability1,2,3,4. No existing electrolyte simultaneously meets all these requirements and electrolyte design is hindered by the absence of an effective guiding principle that addresses the relationships between battery performance, solvation structure and solid-electrolyte-interphase chemistry5. Here we report and validate an electrolyte design strategy based on a group of soft solvents that strikes a balance between weak Li+–solvent interactions, sufficient salt dissociation and desired electrochemistry to fulfil all the aforementioned requirements. Remarkably, the 4.5-volt NMC811||graphite coin cells with areal capacities of more than 2.5milliampere hours per square centimetre retain 75per cent (54per cent) of their room-temperature capacity when these cells are charged and discharged at 50degrees Celsius (60degrees Celsius) at a C rate of 0.1C, and the NMC811||graphite pouch cells with lean electrolyte (2.5grams per ampere hour) achieve stable cycling with an average Coulombic efficiency of more than 99.9per cent at 30degrees Celsius. The comprehensive analysis further reveals an impedance matching between the NMC811 cathode and the graphite anode owing to the formation of similar lithium-fluoride-rich interphases, thus effectively avoiding lithium plating at low temperatures. This electrolyte design principle can be extended to other alkali-metal-ion batteries operating under extreme conditions.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05627-8
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-05627-8
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
