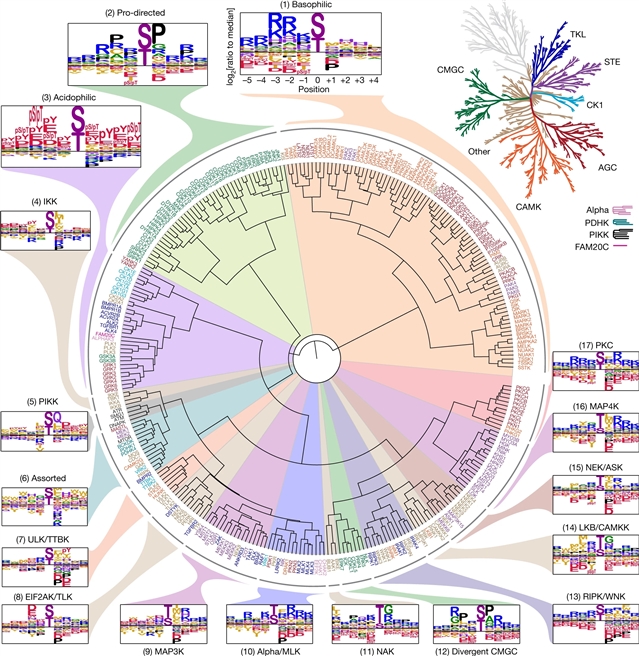
美国康奈尔大学Lewis C. Cantley等研究人员合作绘制出人类丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶组的底物特异性图谱。这一研究成果于2023年1月11日在线发表在国际学术期刊《自然》上。
研究人员使用合成肽库来分析了303个丝氨酸/苏氨酸(Ser/Thr)激酶的底物序列特异性,其中包括超过84%的被预测为在人类中具有活性的激酶。从整体上看,激酶组的底物特异性比预期的要多得多,而且主要是由负选择性驱动。研究人员使用这个全基因组数据集来计算注释和识别能够磷酸化人类Ser/Thr磷蛋白组中每个报告的磷酸化位点的激酶。对于先前已经报道过的一小部分磷酸化位点,研究人员的预测非常一致。当这种方法被应用于研究组织和细胞系对激素、生长因子、靶向抑制剂和环境或遗传扰动的信号反应时,它揭示了对途径复杂性和补偿的意外见解。总的来说,这项研究揭示了人类Ser/Thr激酶组的内在底物特异性,阐明了细胞信号反应,并提供了一个将磷酸化事件与生物途径联系起来的资源。
研究人员表示,蛋白质的磷酸化是生物学中最广泛的翻译后修饰之一。随着基于质谱技术的磷蛋白组学的发展,迄今已确定了90000个丝氨酸和苏氨酸的磷酸化位点,其中几千个与人类疾病和生物过程有关。对于绝大多数的磷酸化事件,目前还不知道人类基因组中编码的300多个蛋白Ser/Thr激酶中哪个负责。
附:英文原文
Title: An atlas of substrate specificities for the human serine/threonine kinome
Author: Johnson, Jared L., Yaron, Tomer M., Huntsman, Emily M., Kerelsky, Alexander, Song, Junho, Regev, Amit, Lin, Ting-Yu, Liberatore, Katarina, Cizin, Daniel M., Cohen, Benjamin M., Vasan, Neil, Ma, Yilun, Krismer, Konstantin, Robles, Jaylissa Torres, van de Kooij, Bert, van Vlimmeren, Anne E., Andre-Busch, Nicole, Kufer, Norbert F., Dorovkov, Maxim V., Ryazanov, Alexey G., Takagi, Yuichiro, Kastenhuber, Edward R., Goncalves, Marcus D., Hopkins, Benjamin D., Elemento, Olivier, Taatjes, Dylan J., Maucuer, Alexandre, Yamashita, Akio, Degterev, Alexei, Uduman, Mohamed, Lu, Jingyi, Landry, Sean D., Zhang, Bin, Cossentino, Ian, Linding, Rune, Blenis, John, Hornbeck, Peter V., Turk, Benjamin E., Yaffe, Michael B., Cantley, Lewis C.
Issue&Volume: 2023-01-11
Abstract: Protein phosphorylation is one of the most widespread post-translational modifications in biology1,2. With advances in mass-spectrometry-based phosphoproteomics, 90,000 sites of serine and threonine phosphorylation have so far been identified, and several thousand have been associated with human diseases and biological processes3,4. For the vast majority of phosphorylation events, it is not yet known which of the more than 300 protein serine/threonine (Ser/Thr) kinases encoded in the human genome are responsible3. Here we used synthetic peptide libraries to profile the substrate sequence specificity of 303 Ser/Thr kinases, comprising more than 84% of those predicted to be active in humans. Viewed in its entirety, the substrate specificity of the kinome was substantially more diverse than expected and was driven extensively by negative selectivity. We used our kinome-wide dataset to computationally annotate and identify the kinases capable of phosphorylating every reported phosphorylation site in the human Ser/Thr phosphoproteome. For the small minority of phosphosites for which the putative protein kinases involved have been previously reported, our predictions were in excellent agreement. When this approach was applied to examine the signalling response of tissues and cell lines to hormones, growth factors, targeted inhibitors and environmental or genetic perturbations, it revealed unexpected insights into pathway complexity and compensation. Overall, these studies reveal the intrinsic substrate specificity of the human Ser/Thr kinome, illuminate cellular signalling responses and provide a resource to link phosphorylation events to biological pathways.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05575-3
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-05575-3
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
